Connecting occipital alpha band peak frequency, visual temporal resolution, and occipital GABA levels in healthy participants and hepatic encephalopathy patients
- PMID: 30109194
- PMCID: PMC6090010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.08.013
Connecting occipital alpha band peak frequency, visual temporal resolution, and occipital GABA levels in healthy participants and hepatic encephalopathy patients
Abstract
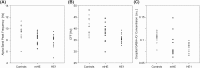
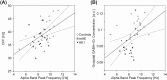
Recent studies have proposed a connection between the individual alpha band peak frequency and the temporal resolution of visual perception in healthy human participants. This connection rests on animal studies describing oscillations in the alpha band as a mode of phasic thalamocortical information transfer for low-level visual stimuli, which critically relies on GABAergic interneurons. Here, we investigated the interplay of these parameters by measuring occipital alpha band peak frequency by means of magnetoencephalography, visual temporal resolution by means of behavioral testing, and occipital GABA levels by means of magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Importantly, we investigated a sample of healthy participants and patients with varying grades of hepatic encephalopathy, which are known to exhibit decreases in the investigated parameters, thus providing an increased parameter space. We found that occipital alpha band peak frequency and visual temporal resolution were positively correlated, i.e., higher occipital alpha band peak frequencies were on average related to a higher temporal resolution. Likewise, occipital alpha band peak frequency correlated positively with occipital GABA levels. However, correlations were significant only when both healthy participants and patients were included in the analysis, thereby indicating a connection of the measures on group level (instead of the individual level). These findings provide new insights into neurophysiological and neurochemical underpinnings of visual perception.
Keywords: Alpha oscillations; CFF, Critical flicker frequency; CSD, Cross-spectral density; EC, Eyes-closed; ECG, Electro-cardiogram; EO, Eyes-open; EOG, Electro-oculogram; GABA; GABA+/Cr, GABA-to creatine -ratio; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; HE, Hepatic encephalopathy; HE1, Clinically manifest HE grade 1; HPI, Head position indication; Hepatic encephalopathy; ICA, Independent component analysis; MEG, Magnetoencephalography; MNI, Montreal Neurological Institute; MRS, Magnetic resonance spectroscopy; Magnetic resonance spectroscopy; Magnetoencephalography; Peak frequency; mHE, Minimal HE.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low visual cortex GABA levels in hepatic encephalopathy: links to blood ammonia, critical flicker frequency, and brain osmolytes.Metab Brain Dis. 2015 Dec;30(6):1429-38. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9729-2. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Metab Brain Dis. 2015. PMID: 26359122
-
Opposite Dynamics of GABA and Glutamate Levels in the Occipital Cortex during Visual Processing.J Neurosci. 2018 Nov 14;38(46):9967-9976. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1214-18.2018. Epub 2018 Oct 3. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30282724 Free PMC article.
-
tDCS Modulates Visual Gamma Oscillations and Basal Alpha Activity in Occipital Cortices: Evidence from MEG.Cereb Cortex. 2018 May 1;28(5):1597-1609. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx055. Cereb Cortex. 2018. PMID: 28334214 Free PMC article.
-
The development of peak alpha frequency from infancy to adolescence and its role in visual temporal processing: A meta-analysis.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2022 Oct;57:101146. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2022.101146. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35973361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-Band Frequency and Temporal Windows in Perception: A Review and Living Meta-analysis of 27 Experiments (and Counting).J Cogn Neurosci. 2024 Apr 1;36(4):640-654. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_02069. J Cogn Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 37856149 Review.
Cited by
-
Self-Directed Neurofeedback Treatment for Subjective Tinnitus Patients Evaluated by Multimodal Functional Imaging.Neural Plast. 2022 Oct 18;2022:5114721. doi: 10.1155/2022/5114721. eCollection 2022. Neural Plast. 2022. PMID: 36304208 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Electroencephalography (EEG) in Combat Sports-Review of Findings, Perspectives, and Limitations.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 10;14(12):4113. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124113. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40565858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic encephalopathy.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022 Jun 23;8(1):43. doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00366-6. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022. PMID: 35739133 Review.
-
Chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging in hepatic encephalopathy.Neuroimage Clin. 2019;22:101743. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101743. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 30856541 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of dynamical degree centrality in brain functional network and its association with metabolic disorder in minimal hepatic encephalopathy.Neuroradiology. 2025 Feb;67(2):371-381. doi: 10.1007/s00234-024-03470-4. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Neuroradiology. 2025. PMID: 39352413
References
-
- Abbasi O., Dammers J., Arrubla J., Warbrick T., Butz M., Neuner I., Shah N.J. Time-frequency analysis of resting state and evoked EEG data recorded at higher magnetic fields up to 9.4T. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2015;255:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Adrian E.D., Matthews B.H. The Berger rhythm: potential changes from the occipital lobes in man. Brain. 1934;57:355–385. - PubMed
-
- Ahveninen J., Lin F.H., Kivisaari R., Autti T., Hämäläinen M., Stufflebeam S., Belliveau J.W., Kähkönen S. MRI-constrained spectral imaging of benzodiazepine modulation of spontaneous neuromagnetic activity in human cortex. NeuroImage. 2007;35:577–582. - PubMed
-
- Aurlien H., Gjerde I., Aarseth J., Eldøen G., Karlsen B., Skeidsvoll H., Gilhus N. EEG background activity described by a large computerized database. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004;115:665–673. - PubMed
-
- Balz J., Keil J., Roa Romero Y., Mekle R., Schubert F., Aydin S., Ittermann B., Gallinat J., Senkowski D. GABA concentration in superior temporal sulcus predicts gamma power and perception in the sound-induced flash illusion. NeuroImage. 2016;125:724–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

