Multi-residue pesticides analysis in water samples using reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC)
- PMID: 30109197
- PMCID: PMC6090086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2018.07.005
Multi-residue pesticides analysis in water samples using reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC)
Abstract
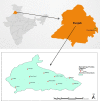
India is one of the leading suppliers of agrochemicals and has the largest pesticide industry in Asia. Among various Indian states, Punjab is the primary user of pesticides. Presence of pesticide residue in water and food products of Punjab is well documented. The present study was designed to envisage the level of pesticide contamination in pond water of eleven villages of Amritsar district of Punjab, India. A rapid and concurrent method for the identification and quantification of pesticides in water samples was developed and validated. The method validation parameters exhibited high sensitivity of the developed method and the proficiency for the identification and quantification of pesticide residues in water samples. The RP-HPLC method described here •is a novel method which is applicable for simple, rapid and precise detection of pesticides.•40.02% of water samples were found contaminated with multi-residue pesticides.•carbofuran was the most abundant pesticide which was present in 18.18% samples.
Keywords: Multi-residue pesticides; Pond water samples; Quantitative analysis; RP-HPLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid determination of residues of pesticides in honey by µGC-ECD and GC-MS/MS: Method validation and estimation of measurement uncertainty according to document No. SANCO/12571/2013.J Environ Sci Health B. 2016;51(3):133-42. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2015.1108748. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Environ Sci Health B. 2016. PMID: 26671720
-
Multi-residue analysis of plant growth regulators and pesticides in traditional Chinese medicines by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 Apr;411(11):2447-2460. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-01691-8. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30859267
-
A multi-residue method for pesticide residue analysis in rice grains using matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Jul;397(6):2181-90. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3645-4. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20379813
-
Current mass spectrometry strategies for the analysis of pesticides and their metabolites in food and water matrices.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2011 Sep-Oct;30(5):907-39. doi: 10.1002/mas.20307. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2011. PMID: 24737632 Review.
-
[Advances on nanoparticles-tagged visual test strips for the rapid detection of pesticides].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Aug;42(16):3056-3064. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170728.010. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29171221 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Environmentally relevant exposures of male mice to carbendazim and thiram cause persistent genotoxicity in male mice.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Apr;27(10):10629-10641. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07088-5. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31940143
-
Recent progress in functional materials for electrochemical detection of pesticides: modification strategies, performance, and future challenges.Anal Sci. 2025 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s44211-025-00838-1. Online ahead of print. Anal Sci. 2025. PMID: 40847219 Review.
-
Appraisal for Edible Use of Vegetable Crops Cultivated in Egypt after Treatment with Selected Insecticides and Fungicides: Insights of Dissipation Rates and Pre-harvest Intervals.Anal Sci. 2021 Dec 10;37(12):1775-1781. doi: 10.2116/analsci.21P176. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Anal Sci. 2021. PMID: 34275969
References
-
- ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Validation of Analytucal Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2(R1) International conference of harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. 2005
-
- Devi P.I. Pesticides in agriculture-a boon or a curse? A case study of Kerala. Econ. Polit. Wkly. 2010:199–207.
-
- Bhardwaj T., Sharma J.P. Impact of pesticides application in agricultural industry: an Indian scenario. Int. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2013;4(8):817–822.
-
- Müller M.H.B., Polder A., Brynildsrud O.B., Karimi M., Lie E., Manyilizu W.B., Mdegela R.H., Mokiti F., Murtadha M., Nonga H.E., Skaare J.U., Lyche J.L. Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in human breast milk and associated health risks to nursing infants in Northern Tanzania. Environ. Res. 2017;154:425–434. - PubMed
-
- Bawa P., Bedi J.S., Gill J.P.S., Aulakh R.S., Kumar A., Arora K. Persistent organic pollutants residues in human breast milk from Bathinda and Ludhiana districts of Punjab, India. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018:1–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources