Fremanezumab blocks CGRP induced dilatation in human cerebral, middle meningeal and abdominal arteries
- PMID: 30109438
- PMCID: PMC6091427
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-018-0905-8
Fremanezumab blocks CGRP induced dilatation in human cerebral, middle meningeal and abdominal arteries
Abstract
Background: Fremanezumab (TEV-48125) is a fully humanized anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibody (mAb) that has shown positive results in the prevention of episodic migraine and chronic migraine. Previous preclinical studies have revealed CGRP antagonistic effects on intracranial arteries (ICA). The aim of the study was to evaluate the in vitro antagonistic effects of fremanezumab on human arteries.
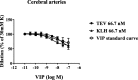
Methods: Arteries were removed in conjunction with neurosurgery (cerebral, CA, and middle meningeal artery, MMA, n = 7) or reconstructive abdominal surgery (abdominal artery, AA, n = 6). Ring segments of the vessels were mounted in a sensitive myograph, the functional responses of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), substance P and CGRP in increasing concentrations (10- 10-10- 7 M) were studied using pre-contraction with 30 mM potassium chloride (KCl). The concentrations of fremanezumab or isotype control antibody (66.7 nM, 0.33 μM, 0.67 μM) were given 30 min prior to CGRP administration.
Results: All included arteries responded with a strong stable contraction to the application of 30 mM KCl. During this pre-contraction, CGRP caused a concentration-dependent relaxation which differed slightly in maximum effect (Imax) between the types of arteries (ICA = 100%; AA 80%). Fremanezumab (66.7 nM) showed a shift in the IC50 value of CGRP, but no significant change in Imax. At higher doses there was also a reduction of Imax. For AA, the Imax decreased from 71% at 66.7 nM, to 4.5% with 0.33 μM of fremanezumab. Isotype control antibody did not modify the responses. There was no effect on concentration-dependent relaxation with VIP with 66.7 nM of fremanezumab or isotype control.
Conclusion: CGRP relaxes pre-contracted human arteries by 80-100%, but with different IC50; the potency range was ICA < AA. The antagonistic effect and potency of fremanezumab was similar, suggesting that there are vasodilatory CGRP receptors present in all studied arteries and that the antibody may have effect in all studied vessels.
Keywords: Antibody; CGRP; CGRP receptor antagonist; Fremanezumab; Human vessels.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the human ethics committee of Lund (LU818–01) and written informed consent was given by all vessel donors.
Competing interests
The authors have nothing to disclose. JS is an employee of TEVA Pharmaceuticals Ltd., but was not involved in the interpretation of the results.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Erenumab (AMG 334), a monoclonal antagonist antibody against the canonical CGRP receptor, does not impair vasodilatory or contractile responses to other vasoactive agents in human isolated cranial arteries.Cephalalgia. 2019 Dec;39(14):1745-1752. doi: 10.1177/0333102419867282. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Cephalalgia. 2019. PMID: 31366221
-
Fremanezumab inhibits vasodilatory effects of CGRP and capsaicin in rat cerebral artery - Potential role in conditions of severe vasoconstriction.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 1;864:172726. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172726. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31589869
-
CSD-Induced Arterial Dilatation and Plasma Protein Extravasation Are Unaffected by Fremanezumab: Implications for CGRP's Role in Migraine with Aura.J Neurosci. 2019 Jul 24;39(30):6001-6011. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0232-19.2019. Epub 2019 May 24. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31127003 Free PMC article.
-
Fremanezumab for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Aug;12(8):741-748. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2019.1635452. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31220963 Review.
-
Fremanezumab as a preventive treatment for episodic and chronic migraine.Expert Rev Neurother. 2019 Aug;19(8):719-728. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2019.1614742. Epub 2019 May 22. Expert Rev Neurother. 2019. PMID: 31043094 Review.
Cited by
-
Mode and site of action of therapies targeting CGRP signaling.J Headache Pain. 2023 Sep 11;24(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01644-8. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37691118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell characterization of the human C2 dorsal root ganglion recovered from C1-2 arthrodesis surgery: implications for neck pain.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 30:2025.03.24.645122. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.24.645122. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40196625 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Improvements across a range of patient-reported domains with fremanezumab treatment: results from a patient survey study.J Headache Pain. 2020 Sep 4;21(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01177-4. J Headache Pain. 2020. PMID: 32887548 Free PMC article.
-
Fremanezumab: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2018 Nov;78(17):1829-1834. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-1004-5. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30406901 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Tolerability of Fremanezumab for Episodic and Chronic Migraine.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023 Feb 20;19:391-401. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S371686. eCollection 2023. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023. PMID: 36846598 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uddman R, Edvinsson L, Ekman R, Kingman T, McCulloch J. Innervation of the feline cerebral vasculature by nerve fibers containing calcitonin gene-related peptide: trigeminal origin and co-existence with substance P. Neurosci Lett. 1985;62(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90296-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Edvinsson L, Fredholm BB, Hamel E, Jansen I, Verrecchia C. Perivascular peptides relax cerebral arteries concomitant with stimulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation or release of an endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1985;58(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90166-1. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

