Novel isatin-derived molecules activate p53 via interference with Mdm2 to promote apoptosis
- PMID: 30109812
- PMCID: PMC6152504
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1506664
Novel isatin-derived molecules activate p53 via interference with Mdm2 to promote apoptosis
Abstract
The p53 protein is a key tumor suppressor in mammals. In response to various forms of genotoxic stress p53 stimulates expression of genes whose products induce cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis. An E3-ubiquitin ligase, Mdm2 (mouse-double-minute 2) and its human ortholog Hdm2, physically interact with the amino-terminus of p53 to mediate its ubiquitin-mediated degradation via the proteasome. Thus, pharmacological inhibition of the p53-Mdm2 interaction leads to overall stabilization of p53 and stimulation of its anti-tumorigenic activity. In this study we characterize the biological effects of a novel class of non-genotoxic isatin Schiff and Mannich base derivatives (ISMBDs) that stabilize p53 on the protein level. The likely mechanism behind their positive effect on p53 is mediated via the competitive interaction with Mdm2. Importantly, unlike Nutlin, these compounds selectively promoted p53-mediated cell death. These novel pharmacological activators of p53 can serve as valuable molecular tools for probing p53-positive tumors and set up the stage for development of new anti-cancer drugs.
Keywords: ISMBDs; Nutlin; Puma; apoptosis; automated microscopy system Operetta; p53-activating molecules.
Figures




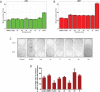
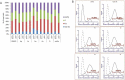
References
-
- Vousden KH, Prives C.. Blinded by the light: the growing complexity of p53. Cell. 2009;137(3):413–431. - PubMed
-
- Barlev N, Sayan B, Candi E, et al. The microRNA and p53 families join forces against cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(2):373. - PubMed
-
- Grossi E, Sánchez Y, Huarte M. Expanding the p53 regulatory network: lncRNAs take up the challenge. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (Bba)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms. 2016;1859(1):200–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
