Effectiveness of nursing intervention for increasing hope in patients with cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 30110091
- PMCID: PMC6091366
- DOI: 10.1590/1518-8345.1920.2937
Effectiveness of nursing intervention for increasing hope in patients with cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: to evaluate the efficacy of nursing interventions to increase the level of hope in cancer patients, in a meta-analysis.
Methods: electronic databases were searched. Two of the authors independently extracted data from the eligible studies, and Stata 13.0 software was used to pool the data.
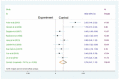
Results: nine randomized controlled trials were included, and methodological quality of each randomized controlled trial (RCT) was evaluated using Cochrane handbook recommendations. A random effects model was used to combine results from eligible studies. The pooled results using the fixed effects model showed that scores to first effects increase significantly after the use of nursing intervention between the groups. Heterogeneity was observed among the studies for posttest (df = 8, P = 0.000; I2 =76.1 %). The results indicated significant heterogeneity across the nine selected studies. The test for heterogeneity showed no homogeneity among studies for follow-up (df = 8, P = 0.328; I2 = 12.9 %), and there was no statistical significance.
Conclusion: the current evidence suggests that nursing intervention has a positive effect on hope in cancer patients. However, more large-scale and high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm these results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effects of spiritual interventions in patients with cancer: a meta-analysis.Oncol Nurs Forum. 2014 Sep;41(5):E290-301. doi: 10.1188/14.ONF.E290-E301. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2014. PMID: 25158666
-
Effectiveness of flipped classrooms in Chinese baccalaureate nursing education: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int J Nurs Stud. 2018 Mar;79:94-103. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2017.11.012. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018. PMID: 29223013 Review.
-
The Effectiveness of Psychoeducational Interventions Focused on Sexuality in Cancer.Cancer Nurs. 2015 Sep-Oct;38(5):E32-42. doi: 10.1097/NCC.0000000000000212. Cancer Nurs. 2015. PMID: 25521909 Review.
-
Nursing intervention to increase hope and quality of life in newly diagnosed cancer patients.Cancer Nurs. 1998 Aug;21(4):235-45. doi: 10.1097/00002820-199808000-00003. Cancer Nurs. 1998. PMID: 9691504 Clinical Trial.
-
Nursing intervention to increase hope in cancer patients.J Clin Nurs. 1998 Jan;7(1):19-27. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2702.1998.00126.x. J Clin Nurs. 1998. PMID: 9510704
Cited by
-
The effect of individual nursing on improving the living ability and blood sugar control of Alzheimer disease patients with diabetes mellitus.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):9324-9331. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34540049 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of high-quality nursing on negative emotions and hope levels of patients undergoing oral and maxillofacial surgery.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):9722-9728. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34540101 Free PMC article.
-
Nursing model based on Snyder's hope theory in emergency care of patients with acute myocardial infarction.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jul 15;15(7):4770-4778. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37560221 Free PMC article.
-
Is Advance Care Planning Associated With Decreased Hope in Advanced Cancer?JCO Oncol Pract. 2021 Feb;17(2):e248-e256. doi: 10.1200/OP.20.00039. Epub 2020 Jun 12. JCO Oncol Pract. 2021. PMID: 32530807 Free PMC article.
-
Fatigue in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing radiation therapy: a prospective study.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2019 Aug 19;27:e3168. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.2813-3168. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2019. PMID: 31432921 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

