Optimization of fluorophores for chemical tagging and immunohistochemistry of Drosophila neurons
- PMID: 30110347
- PMCID: PMC6093644
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200759
Optimization of fluorophores for chemical tagging and immunohistochemistry of Drosophila neurons
Abstract
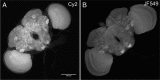
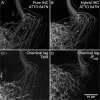
The use of genetically encoded 'self-labeling tags' with chemical fluorophore ligands enables rapid labeling of specific cells in neural tissue. To improve the chemical tagging of neurons, we synthesized and evaluated new fluorophore ligands based on Cy, Janelia Fluor, Alexa Fluor, and ATTO dyes and tested these with recently improved Drosophila melanogaster transgenes. We found that tissue clearing and mounting in DPX substantially improves signal quality when combined with specific non-cyanine fluorophores. We compared and combined this labeling technique with standard immunohistochemistry in the Drosophila brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Coons AH, Creech HJ, Jones RN, 1941. Immunological Properties of an Antibody Containing a Fluorescent Group. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1941; 47: 200–202.
-
- Erichsen JT, Reiner A, Karten HJ. Co-occurrence of substance P-like and Leu-enkephalin-like immunoreactivities in neurones and fibres of avian nervous system. Nature. 1982; 295: 407–10. - PubMed
-
- Mayersbach HV. Principles and limitations of immunohistochemical methods. J R Microsc Soc. 1967; 87: 295–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

