Smoking Cessation, Weight Change, Type 2 Diabetes, and Mortality
- PMID: 30110591
- PMCID: PMC6165582
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1803626
Smoking Cessation, Weight Change, Type 2 Diabetes, and Mortality
Abstract
Background: Whether weight gain after smoking cessation attenuates the health benefits of quitting is unclear.
Methods: In three cohort studies involving men and women in the United States, we identified those who had reported quitting smoking and we prospectively assessed changes in smoking status and body weight. We estimated risks of type 2 diabetes, death from cardiovascular disease, and death from any cause among those who had reported quitting smoking, according to weight changes after smoking cessation.
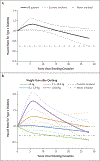
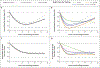
Results: The risk of type 2 diabetes was higher among recent quitters (2 to 6 years since smoking cessation) than among current smokers (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.12 to 1.32). The risk peaked 5 to 7 years after quitting and then gradually decreased. The temporary increase in the risk of type 2 diabetes was directly proportional to weight gain, and the risk was not increased among quitters without weight gain (P<0.001 for interaction). In contrast, quitters did not have a temporary increase in mortality, regardless of weight change after quitting. As compared with current smokers, the hazard ratios for death from cardiovascular disease were 0.69 (95% CI, 0.54 to 0.88) among recent quitters without weight gain, 0.47 (95% CI, 0.35 to 0.63) among those with weight gain of 0.1 to 5.0 kg, 0.25 (95% CI, 0.15 to 0.42) among those with weight gain of 5.1 to 10.0 kg, 0.33 (95% CI, 0.18 to 0.60) among those with weight gain of more than 10.0 kg, and 0.50 (95% CI, 0.46 to 0.55) among longer-term quitters (>6 years since smoking cessation). Similar associations were observed for death from any cause.
Conclusions: Smoking cessation that was accompanied by substantial weight gain was associated with an increased short-term risk of type 2 diabetes but did not mitigate the benefits of quitting smoking on reducing cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health.).
Figures
Comment in
-
Heavier but Healthier - Diabetes and Smoking Cessation.N Engl J Med. 2018 Aug 16;379(7):684-685. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1809004. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 30110593 No abstract available.
-
Nach Rauchstopp etwas dicker? Egal!MMW Fortschr Med. 2018 Nov;160(19):34. doi: 10.1007/s15006-018-1078-8. MMW Fortschr Med. 2018. PMID: 30406539 German. No abstract available.
-
Smoking and Other Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 27;379(26):2572-2573. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1812842. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 30586511 No abstract available.
-
Smoking and Other Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2018 Dec 27;379(26):2573. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1812842. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 30586512 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jha P, Ramasundarahettige C, Landsman V, et al. 21st-century hazards of smoking and benefits of cessation in the United States. N Engl J Med 2013;368:341–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
