Comprehensive Analysis of Codon Usage on Rabies Virus and Other Lyssaviruses
- PMID: 30110957
- PMCID: PMC6121662
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19082397
Comprehensive Analysis of Codon Usage on Rabies Virus and Other Lyssaviruses
Abstract
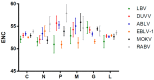
Rabies virus (RABV) and other lyssaviruses can cause rabies and rabies-like diseases, which are a persistent public health threat to humans and other mammals. Lyssaviruses exhibit distinct characteristics in terms of geographical distribution and host specificity, indicative of a long-standing diversification to adapt to the environment. However, the evolutionary diversity of lyssaviruses, in terms of codon usage, is still unclear. We found that RABV has the lowest codon usage bias among lyssaviruses strains, evidenced by its high mean effective number of codons (ENC) (53.84 ± 0.35). Moreover, natural selection is the driving force in shaping the codon usage pattern of these strains. In summary, our study sheds light on the codon usage patterns of lyssaviruses, which can aid in the development of control strategies and experimental research.
Keywords: RABV; codon usage bias; lyssaviruses; natural selection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Codon usage bias in the N gene of rabies virus.Infect Genet Evol. 2017 Oct;54:458-465. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Infect Genet Evol. 2017. PMID: 28818621
-
Analyzing the Evolution and Host Adaptation of the Rabies Virus from the Perspective of Codon Usage Bias.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023 Oct 10;2023:4667253. doi: 10.1155/2023/4667253. eCollection 2023. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023. PMID: 40303686 Free PMC article.
-
Synonymous codon usage pattern in glycoprotein gene of rabies virus.Gene. 2016 Jun 10;584(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.02.047. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26945626
-
The spread and evolution of rabies virus: conquering new frontiers.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018 Apr;16(4):241-255. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2018.11. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29479072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular epidemiology of lyssaviruses in Eurasia.Dev Biol (Basel). 2008;131:125-31. Dev Biol (Basel). 2008. PMID: 18634471 Review.
Cited by
-
Codon usage bias analysis of the gene encoding NAD+-dependent DNA ligase protein of Invertebrate iridescent virus 6.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Oct 9;205(11):352. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03688-5. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37812231
-
Comparative genomics of hepatitis A virus, hepatitis C virus, and hepatitis E virus provides insights into the evolutionary history of Hepatovirus species.Microbiologyopen. 2020 Feb;9(2):e973. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.973. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Microbiologyopen. 2020. PMID: 31742930 Free PMC article.
-
Edging on Mutational Bias, Induced Natural Selection From Host and Natural Reservoirs Predominates Codon Usage Evolution in Hantaan Virus.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jul 2;12:699788. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.699788. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34276633 Free PMC article.
-
Codon Usage of Hepatitis E Viruses: A Comprehensive Analysis.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 21;13:938651. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.938651. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35801104 Free PMC article.
-
Codon usage of host-specific P genotypes (VP4) in group A rotavirus.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jul 16;23(1):518. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08730-2. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35842571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hampson K., Coudeville L., Lembo T., Sambo M. Selected highlights from other journals: Estimating the global burden of canine rabies. Vet. Rec. 2015;178:599.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

