Safety and efficacy of ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer drug-eluting stents: a meta-analysis of randomized trials
- PMID: 30111289
- PMCID: PMC6094581
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-018-0902-5
Safety and efficacy of ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer drug-eluting stents: a meta-analysis of randomized trials
Abstract
Background: The Orsiro biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent (O-SES) is a new-generation biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stent with the thinnest strut thickness to date developed to improve the percutaneous treatment of patients with coronary artery disease. We perform a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) comparing the efficacy and safety of an ultra-thin, Orsiro biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent (O-SES) compared with durable polymer drug-eluting stents (DP-DESs).
Methods: Medline, Embase, and CENTRAL databases were searched for randomized controlled trials comparing the safety and efficacy of O-SES versus DP-DES. Paired reviewers independently screened citations, assessed risk of bias of included studies, and extracted data. We used the Mantel-Haenszel method to calculate risk ratio (RR) by means of a random-effects model.
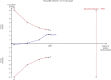
Results: Six RCTs with a total of 6949 patients were selected. All included trials were rated as low risk of bias. The O-SES significantly reduced the risk of myocardial infarction (RR 0.78, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.62-0.98; I2 = 0%; 10 fewer per 1000 [from 1 fewer to 18 fewer]; high quality) compared with the DP-DES. There was no significant difference between O-SES and DP-DES in the prevention of stent thrombosis (RR: 0.75; 95% CI: 0.52-1.08), cardiac death (RR: 0.93; 95% CI: 0.63-1.36), target lesion revascularization (RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.86-1.42) and target vessel revascularization (RR 0.97, 95% CI 0.78-1.21).
Conclusion: Among patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, O-SES resulted in significantly lower rates of myocardial infarction than DP-DES and had a trend toward reduction in stent thrombosis.
Keywords: Biodegradable polymer; Durable polymer; Meta-analysis; Percutaneous coronary intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ultrathin Strut Biodegradable Polymer Sirolimus-Eluting Stent Versus Durable-Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stent for Percutaneous Coronary Revascularization: 2-Year Results of the BIOSCIENCE Trial.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Mar 15;5(3):e003255. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003255. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 26979080 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Improved safety and reduction in stent thrombosis associated with biodegradable polymer-based biolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer-based sirolimus-eluting stents in patients with coronary artery disease: final 5-year report of the LEADERS (Limus Eluted From A Durable Versus ERodable Stent Coating) randomized, noninferiority trial.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Aug;6(8):777-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.04.011. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013. PMID: 23968698 Clinical Trial.
-
Unselected Use of Ultrathin Strut Biodegradable Polymer Sirolimus-Eluting Stent Versus Durable Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stent for Coronary Revascularization.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018 Sep;11(9):e006741. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.118.006741. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018. PMID: 30354590
-
A comparison of the ultrathin Orsiro Hybrid sirolimus-eluting stent with contemporary drug-eluting stents: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2018 Jan;19(1 Pt A):5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2017.11.009. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29221958 Review.
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety between ultrathin bioresorbable polymer sirolimus-eluting stents and thin durable polymer drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature.Coron Artery Dis. 2019 Dec;30(8):590-599. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000797. Coron Artery Dis. 2019. PMID: 31609756
Cited by
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells in intimal hyperplasia, an update.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 4;13:1081881. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1081881. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36685215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Procedural safety and outcome of ultrathin strut stents (<60 μm) in the management of very long coronary artery stenosis (>30 mm) - A retrospective real world study.Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Aug 15;10(3):182-188. eCollection 2020. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32923099 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrathin-strut versus thin-strut stent healing and outcomes in preclinical and clinical subjects.EuroIntervention. 2024 May 20;20(10):e669-e680. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-23-00563. EuroIntervention. 2024. PMID: 38776143 Free PMC article.
-
Individual patient data analysis of the BIOFLOW study program comparing safety and efficacy of a bioresorbable polymer sirolimus eluting stent to a durable polymer everolimus eluting stent.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021 Nov 1;98(5):848-856. doi: 10.1002/ccd.29254. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021. PMID: 32890442 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Durable versus biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stents in all-comers.Open Heart. 2025 Mar 3;12(1):e003104. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2024-003104. Open Heart. 2025. PMID: 40032607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Navarese EP, Tandjung K, Claessen B, Andreotti F, Kowalewski M, Kandzari DE, Kereiakes DJ, Waksman R, Mauri L, Meredith IT, et al. Safety and efficacy outcomes of first and second generation durable polymer drug eluting stents and biodegradable polymer biolimus eluting stents in clinical practice: comprehensive network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;347:f6530. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f6530. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kang SH, Park KW, Kang DY, Lim WH, Park KT, Han JK, Kang HJ, Koo BK, Oh BH, Park YB, et al. Biodegradable-polymer drug-eluting stents vs. bare metal stents vs. durable-polymer drug-eluting stents: a systematic review and Bayesian approach network meta-analysis. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(17):1147–1158. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht570. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

