Nomogram for prediction of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy in juvenile-onset type 1 diabetes: a cohort study in an Asian population
- PMID: 30111889
- PMCID: PMC6093915
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30521-7
Nomogram for prediction of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy in juvenile-onset type 1 diabetes: a cohort study in an Asian population
Abstract
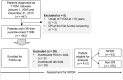
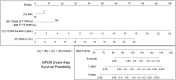
The need for screening for retinopathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) has been emphasised, but diagnostic delays were reported when screening was done at fixed intervals. To establish an individualised risk-prediction model to assist screening non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) in T1DM, we performed a retrospective cohort study enrolling participants in the Chang Gung Juvenile Diabetes Eye Study. There were 413 patients with 12 381 records analysed from 2005 to 2015. A time-dependent Cox proportional hazard analysis was used to evaluate the risks of NPDR development and a nomogram with risk-stratification indicators was established based on the results. During 97 months of follow-up, 43 of 413 patients (10.4%) developed NPDR. Male sex (HR: 0.4, 95% CI: 0.19-0.85), age 5-14 years at onset of T1DM (6.38, 2.41-16.87), duration of diabetes (1.57, 1.41-1.75), and hemoglobin A1c level (1.56, 1.35-1.80) were independently associated with NPDR. Using the nomogram offers a quick method in the clinical setting to interpret the risk of NPDR development. Based on its weighting, each of the independent factors is allocated a score, and the total points indicate the probabilities of NPDR occurring within 6 months, 1 year, and 3 years.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

