MIST1 regulates SNAI1 and acts through the PTEN/AKT signaling axis to promote anoikisresistance in human melanoma cells
- PMID: 30112032
- PMCID: PMC6090440
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6225
MIST1 regulates SNAI1 and acts through the PTEN/AKT signaling axis to promote anoikisresistance in human melanoma cells
Erratum in
-
Erratum: MIST1 regulates SNAI1 and acts through the PTEN/AKT signaling axis to promote anoikis resistance in human melanoma cells.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jan;21(1):46. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9481. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33365056 Free PMC article.
Abstract
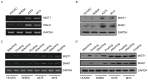
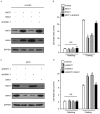
Cutaneous malignant melanoma (CMM) is one of the most dangerous types of skin cancer. The prognosis of CMM patients with ulcers, regional lymph node metastasis or organ metastasis is poor. In this process, resistance to anoikis is a critical step in tumor cell metastasis. Tumor cells survive in the vascular and lymphatic system through the escape of anoikis to finally form clones in the distal tissue. The present study revealed that muscle intestine and stomach expression 1 (MIST1), a secreting cell-restricted transcription factor, was overexpressed in melanoma cells. At the same time, the expression of SNAI1 was also high. High expression of MIST1 and SNAI1 all contributed to melanoma cells bypassing anoikis. By changing the expression of MIST1, SNAI1 was indicated to be a downstream gene of MIST1. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter gene technology revealed that MIST1 promoted the expression of SNAI1 by directly binding to its promoter region. Furthermore, inhibition of the phosphorylation/activity of Akt by LY294002 and knockdown of phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) with simultaneous upregulation or knockdown of MIST1 revealed that SNAI1 improved the phosphorylation of Akt by inhibiting the expression of PTEN. These results suggested that MIST1 hijacked the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway through directly regulating SNAI1 and affected the anoikis resistance capacity of melanoma cells.
Keywords: AKT; anoikis; melanoma; muscle intestine and stomach expression 1; phosphatase and tensin homologue; transcriptional regulation.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
