Association between Y-Maze Acquisition Learning and Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Polymorphisms in Mice
- PMID: 30112411
- PMCID: PMC6077659
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6381932
Association between Y-Maze Acquisition Learning and Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Polymorphisms in Mice
Abstract
Objective: To explore the association between the acquisition process in the Y-maze and H-2 class II polymorphisms in mice.
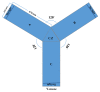
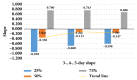
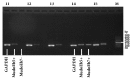
Methods: Mice were trained for 5 consecutive days in the Y-maze. The value of the slope of the latent period was considered an indication for the acquisition process. A slope < 0 indicated learning during the training and a slope > 0 indicated no learning. The H-2 polymorphism was determined with PCR amplification, and the correlation between the alleles and the acquisition process was analyzed.
Results: The overall percentage of mice that learned was 46.1%. The percentage of mice that had learned with MudoEb5 (37.9%) was significantly lower than that of mice without MudoEb5 (61.1%; P < 0.05). The percentage of mice that had learned with MudoEb7 (26.1%) was significantly lower than that of mice without MudoEb7 (51.9%; P < 0.05).
Conclusions: The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and other alleles may be involved in the acquisition process. There may be a biological basis for learning in mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Presentation of a self-peptide for in vivo tolerance induction of CD4+ T cells is governed by a processing factor that maps to the class II region of the major histocompatibility complex locus.J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1481-91. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1481. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7595218 Free PMC article.
-
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Genes and Disease Resistance in Fish.Cells. 2019 Apr 25;8(4):378. doi: 10.3390/cells8040378. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31027287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HLA class II polymorphism: implications for genetic susceptibility to autoimmune disease.Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):5-19. Lab Invest. 1989. PMID: 2664347 Review.
-
Ancestral polymorphisms of MHC class II genes: divergent allele advantage.Immunol Res. 1990;9(2):115-22. doi: 10.1007/BF02918202. Immunol Res. 1990. PMID: 2189934 Review. No abstract available.
-
The influence of MHC and non-MHC genes on the nature of murine cardiac allograft rejection. I. Kinetic analysis of mononuclear cell infiltrate and MHC-class I/class II expression in donor tissue.Transplantation. 1990 Aug;50(2):313-24. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199008000-00028. Transplantation. 1990. PMID: 2200176
Cited by
-
Attenuation of Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia via Cholinergic Modulation in Mice by Synthetic Curcumin Analogs.Molecules. 2022 Apr 11;27(8):2468. doi: 10.3390/molecules27082468. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35458662 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Mono-Carbonyl Curcumin Analogues Attenuate Oxidative Stress in Mouse Models.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 17;10(10):2597. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102597. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289859 Free PMC article.
-
3-O-Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid ameliorates acquired, consolidated and recognitive memory deficits through the regulation of hippocampal PPAR γ, MMP9 and MMP2 genes in dementia model.Heliyon. 2021 Dec 2;7(12):e08523. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08523. eCollection 2021 Dec. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34926858 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Amide Proton Transfer Imaging of Rat With Alzheimer's Disease Using Saturation With Frequency Alternating RF Irradiation Method.Front Aging Neurosci. 2019 Aug 22;11:217. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00217. eCollection 2019. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31507405 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Dapsone on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice: Involvement of Nitric Oxide Pathway.Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2022 Mar 24;12(1):43-50. doi: 10.1159/000522163. eCollection 2022 Jan-Apr. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2022. PMID: 35611148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hall J., Thomas K. L., Everitt B. J. Cellular imaging of zif268 expression in the hippocampus and amygdala during contextual and cued fear memory retrieval: selective activation of hippocampal CA1 neurons during the recall of contextual memories. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2001;21(6):2186–2193. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-06-02186.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials