Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
- PMID: 30113146
- PMCID: PMC6202557
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0017
Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Abstract
Background: This report presents the recent prevalence and comorbidities related to diabetes in Korea by analyzing the nationally representative data.
Methods: Using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 2013 to 2014, the percentages and the total number of subjects over the age of 30 years with diabetes and prediabetes were estimated and applied to the National Population Census in 2014. Diagnosis of diabetes was based on fasting plasma glucose (≥126 mg/dL), current taking of antidiabetic medication, history of previous diabetes, or glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%. Impaired fasting glucose (IFG) was defined by fasting plasma glucose in the range of 100 to 125 mg/dL among those without diabetes.
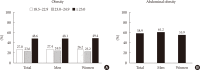
Results: About 4.8 million (13.7%) Korean adults (≥30 years old) had diabetes, and about 8.3 million (24.8%) Korean adults had IFG. However, 29.3% of the subjects with diabetes are not aware of their condition. Of the subjects with diabetes, 48.6% and 54.7% were obese and hypertensive, respectively, and 31.6% had hypercholesterolemia. Although most subjects with diabetes (89.1%) were under medical treatment, and mostly being treated with oral hypoglycemic agents (80.2%), 10.8% have remained untreated. With respect to overall glycemic control, 43.5% reached the target of HbA1c <7%, whereas 23.3% reached the target when the standard was set to HbA1c <6.5%, according to the Korean Diabetes Association guideline.
Conclusion: Diabetes is a major public health threat in Korea, but a significant proportion of adults were not controlling their illness. We need comprehensive approaches to overcome the upcoming diabetes-related disease burden in Korea.
Keywords: Comorbidity; Diabetes mellitus; Glycated hemoglobin A; Prediabetic state; Prevalence; Public health; Republic of Korea.
Copyright © 2018 Korean Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, Cavan D, Shaw JE, Makaroff LE. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40–50. - PubMed
-
- Shin HY, Lee JY, Song J, Lee S, Lee J, Lim B, Kim H, Huh S. Cause-of-death statistics in the Republic of Korea, 2014. J Korean Med Assoc. 2016;59:221–232.
-
- Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972;18:499–502. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

