Sexual behavior across the transition to adulthood and sexually transmitted infections: Findings from the national survey of human papillomavirus prevalence (POP-Brazil)
- PMID: 30113461
- PMCID: PMC6112916
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011758
Sexual behavior across the transition to adulthood and sexually transmitted infections: Findings from the national survey of human papillomavirus prevalence (POP-Brazil)
Abstract
The sexual behaviors of 15- to 24-year-olds increase the risk of this population to acquire sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The present study aimed to describe the sexual behavior in the transition to adulthood Brazilian population and its association with STI history.We analyzed cross-sectional data collected from 8562 sexually active women and men who participated in the National Survey of Human Papillomavirus Prevalence (POP-Brazil). This large-scale survey enrolled participants from 26 Brazilian capitals and the Federal District. Professionals from primary care facilities were trained to collect data utilizing a standardized questionnaire with questions on sociodemographic, sexual behavior, and drug use. We constructed a Poisson model with robust variance for both crude and adjusted analysis to investigate the associations between the variables. To adjust the distribution of the sample to the study population, we weighted the measures by the population size in each city and by gender.There were differences in several aspects from sexual behavior between genders. The majority of men reported an early sexual initiation, more sexual partners, and a different practice in sexual positions when compared with women. Women reported use of contraception more frequently than men (P < .001). The use of alcohol and drugs and the use of drugs before sexual intercourse impact in STIs equally between the genders. Exclusive for women, the presence of any STI was associated with the practice of vaginal sex and other types of intercourse (adjusted prevalence ratio [APR] 1.43, 95% CI 1.08-1.88). For men, the number of sexual partners in the last year (APR 1.02, 95% CI 1.01-1.04), not having vaginal sex (APR 3.25, 95% CI 1.78-5.92) and sexual experience with someone of the same sex (APR 4.05, 95% CI, 2.88-5.70) were associated with a higher presence of STIs.This is the first report regarding sexual behavior in a nationally representative population sample in Brazil. This study provides more valid estimates of sexual behavior and associated STIs, identifying important differences in sexual behavior and identifying predictors for referred STIs among females and males.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: CD, AGKM, FMAS, and ASB work for the Ministry of Health of Brazil. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
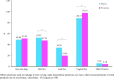
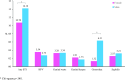
References
-
- Vasilenko SA, Linden-Carmichael A, Lanza ST, et al. Sexual behavior and heavy episodic drinking across the transition to adulthood: differences by college attendance. J Res Adolesc 2017;28:473–87. Available at: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/jora.12348. Access in April 2018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wong CF, Schrager SM, Chou C-P, et al. Changes in developmental contexts as predictors of transitions in HIV-risk behaviors among young men who have sex with men (YMSM). Am J Community Psychol 2013;51:439–50. - PubMed
-
- Siracusano S, Silvestri T, Casotto D. Sexually transmitted diseases: epidemiological and clinical aspects in adults. Riv Urol 2014;81:200–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

