The association between blood pressure and long-term outcomes of patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy with and without surgical revascularization: an analysis of the STICH trial
- PMID: 30113633
- PMCID: PMC6166135
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy438
The association between blood pressure and long-term outcomes of patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy with and without surgical revascularization: an analysis of the STICH trial
Abstract
Aims: Hypertension (HTN) is a well-known contributor to cardiovascular disease, including heart failure (HF) and coronary artery disease, and is the leading risk factor for premature death world-wide. A J- or U-shaped relationship has been suggested between blood pressure (BP) and clinical outcomes in different studies. However, there is little information about the significance of BP on the outcomes of patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction. This study aimed to determine the relationship between BP and mortality outcomes in patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy.
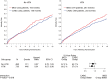
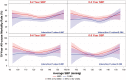
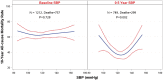
Methods and results: The influence of BP during a median follow-up of 9.8 years was studied in a total of 1212 patients with ejection fraction ≤35% and coronary disease amenable to coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) who were randomized to CABG or medical therapy alone (MED) in the STICH (Surgical Treatment for Ischaemic Heart Failure) trial. Landmark analyses were performed starting at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years after randomization, in which previous systolic BP values were averaged and related to subsequent mortality through the end of follow-up with a median of 9.8 years. Neither a previous history of HTN nor baseline BP had any significant influence on long-term mortality outcomes, nor did they have a significant interaction with MED or CABG treatment. The landmark analyses showed a progressive U-shaped relationship that became strongest at 5 years (χ2 and P-values: 7.08, P = 0.069; 8.72, P = 0.033; 9.86; P = 0.020; 8.31, P = 0.040; 14.52, P = 0.002; at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5-year landmark analyses, respectively). The relationship between diastolic BP (DBP) and outcomes was similar. The most favourable outcomes were observed in the SBP range 120-130, and DBP 75-85 mmHg, whereas lower and higher BP were associated with worse outcomes. There were no differences in BP-lowering medications between groups.
Conclusion: A strong U-shaped relationship between BP and mortality outcomes was evident in ischaemic HF patients. The results imply that the optimal SBP might be in the range 120-130 mmHg after intervention, and possibly be subject to pharmacologic action regarding high BP. Further, low BP was a marker of poor outcomes that might require other interactions and treatment strategies.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00023595.
Figures



References
-
- GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017;390:1345–1422. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Liu P, Roth GA, Ng M, Biryukov S, Marczak L, Alexander L, Estep K, Hassen Abate K, Akinyemiju TF, Ali R, Alvis-Guzman N, Azzopardi P, Banerjee A, Barnighausen T, Basu A, Bekele T, Bennett DA, Biadgilign S, Catala-Lopez F, Feigin VL, Fernandes JC, Fischer F, Gebru AA, Gona P, Gupta R, Hankey GJ, Jonas JB, Judd SE, Khang YH, Khosravi A, Kim YJ, Kimokoti RW, Kokubo Y, Kolte D, Lopez A, Lotufo PA, Malekzadeh R, Melaku YA, Mensah GA, Misganaw A, Mokdad AH, Moran AE, Nawaz H, Neal B, Ngalesoni FN, Ohkubo T, Pourmalek F, Rafay A, Rai RK, Rojas-Rueda D, Sampson UK, Santos IS, Sawhney M, Schutte AE, Sepanlou SG, Shifa GT, Shiue I, Tedla BA, Thrift AG, Tonelli M, Truelsen T, Tsilimparis N, Ukwaja KN, Uthman OA, Vasankari T, Venketasubramanian N, Vlassov VV, Vos T, Westerman R, Yan LL, Yano Y, Yonemoto N, Zaki ME, Murray CJ.. Global burden of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of at least 110 to 115 mmHg, 1990-2015. JAMA 2017;317:165–182. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F, Redon J, Dominiczak A, Narkiewicz K, Nilsson PM, Burnier M, Viigimaa M, Ambrosioni E, Caufield M, Coca A, Olsen MH, Schmieder RE, Tsioufis C, van de BP, Zamorano JL, Achenbach S, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Fagard R, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Sirnes PA, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, Clement DL, Coca A, Gillebert TC, Tendera M, Rosei EA, Ambrosioni E, Anker SD, Bauersachs J, Hitij JB, Caulfield M, De Buyzere M, De Geest S, Derumeaux GA, Erdine S, Farsang C, Funck-Brentano C, Gerc V, Germano G, Gielen S, Haller H, Hoes AW, Jordan J, Kahan T, Komajda M, Lovic D, Mahrholdt H, Olsen MH, Ostergren J, Parati G, Perk J, Polonia J, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Ryden L, Sirenko Y, Stanton A, Struijker-Boudier H, Tsioufis C, van de Borne P, Vlachopoulos C, Volpe M, Wood DA.. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2013;34:2159–2219. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Dans T, Avezum A, Lanas F, McQueen M, Budaj A, Pais P, Varigos J, Lisheng L.. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. Lancet 2004;364:937–952. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Rangarajan S, Teo K, Islam S, Li W, Liu L, Bo J, Lou Q, Lu F, Liu T, Yu L, Zhang S, Mony P, Swaminathan S, Mohan V, Gupta R, Kumar R, Vijayakumar K, Lear S, Anand S, Wielgosz A, Diaz R, Avezum A, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Lanas F, Yusoff K, Ismail N, Iqbal R, Rahman O, Rosengren A, Yusufali A, Kelishadi R, Kruger A, Puoane T, Szuba A, Chifamba J, Oguz A, McQueen M, McKee M, Dagenais G, Investigators P.. Cardiovascular risk and events in 17 low-, middle-, and high-income countries. N Engl J Med 2014;371:818–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

