Expression of Non-collagenous Bone Matrix Proteins in Osteoblasts Stimulated by Mechanical Stretching in the Cranial Suture of Neonatal Mice
- PMID: 30113872
- PMCID: PMC6354315
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155418793588
Expression of Non-collagenous Bone Matrix Proteins in Osteoblasts Stimulated by Mechanical Stretching in the Cranial Suture of Neonatal Mice
Abstract
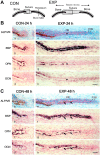
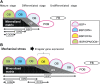
We investigated the influence of mechanical stretching on the genetic expression pattern of non-collagenous bone matrix proteins in osteoblasts. The cranial sutures of neonatal mice were subjected to ex vivo mechanical stretching. In the non-stretched control group, as osteoblast differentiation progressed, the successive genetic expression of bone sialoprotein (BSP), osteopontin (OPN), and osteocalcin (OCN) was detected using in situ hybridization, in that order. In the stretched group, the sutures were widened, and after 24 hr of cultivation, a large number of osteoblasts and abundant new osteoid were observed on the borders of the parietal bones. All new osteoblasts expressed BSP and some of them expressed OPN, but very few of them expressed OCN. After 48 hr, more extensive presence of osteoid was noted on the borders of the parietal bones, and this osteoid was partially mineralized; all osteoblasts on the osteoid surface expressed BSP, and more osteoblasts expressed OPN than those after 24 hr cultivation. Surprisingly, many of the osteoblasts that did not express OPN, expressed OCN. This suggests that when osteoblast differentiation is stimulated by mechanical stress, the genetic expression pattern of non-collagenous proteins in the newly differentiated osteoblasts is affected.
Keywords: mechanical loading; non-collagenous bone proteins; ossification; sagittal sutures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Bouleftour W, Juignet L, Bouet G, Granito RN, Vanden-Bossche A, Laroche N, Aubin JE, Lafage-Proust MH, Vico L, Malaval L. The role of the SIBLING, Bone Sialoprotein in skeletal biology—contribution of mouse experimental genetics. Matrix Biol. 2016;52–54:60–77. - PubMed
-
- Hunter GK. Role of osteopontin in modulation of hydroxyapatite formation. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;93(4):348–54. - PubMed
-
- Denhardt DT, Giachelli CM, Rittling SR. Role of osteopontin in cellular signaling and toxicant injury. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:723–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

