HCV elimination among people who inject drugs. Modelling pre- and post-WHO elimination era
- PMID: 30114207
- PMCID: PMC6095544
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202109
HCV elimination among people who inject drugs. Modelling pre- and post-WHO elimination era
Abstract
Background: Elimination of hepatitis C virus (HCV) among people who inject drugs (PWID) is a costly investment, so strategies should not only focus on eliminating the disease, but also on preventing disease resurgence. The aims of this study are to compute the minimum necessary antiviral therapies to achieve elimination with and without the additional expansion of harm reduction (HR) programs and to examine the sustainability of HCV elimination after 2030 if treatment is discontinued.
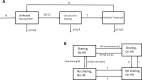
Method: We considered two types of epidemic (with low (30%) and high (50%) proportion of PWID who engage in sharing equipment (sharers)) within three baseline chronic HCV (CHC) prevalence settings (30%, 45% and 60%), assuming a baseline HR coverage of 40%. We define sustainable elimination strategies, those that could maintain eliminations results for a decade (2031-2040), in the absence of additional treatment.
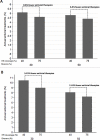
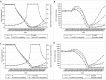
Results: The model shows that the optimum elimination strategy is dependent on risk sharing behavior of the examined population. The necessary annual treatment coverage to achieve HCV elimination under 45% baseline CHC prevalence, without the simultaneous expansion of HR programs, ranges between 4.7-5.1%. Similarly, under 60% baseline CHC prevalence the needed treatment coverage varies from 9.0-10.5%. Increasing HR coverage from 40% to 75%, reduces the required treatment coverage by 6.5-9.8% and 11.0-15.0% under 45% or 60% CHC prevalence, respectively. In settings with ≤45% baseline CHC prevalence, expanding HR to 75% could prevent the disease from rebounding after elimination, irrespective of the type of the epidemic. In high chronic HCV prevalence, counseling interventions to reduce sharing are also needed to maintain the HCV incident cases in low levels.
Conclusions: Harm reduction strategies have a vital role in HCV elimination strategy, as they reduce the required number of treatments to eliminate HCV and they provide sustainability after the elimination. The above underlines that HCV elimination strategies should be built upon the existing HR services, and argue for HR expansion in countries without services.
Conflict of interest statement
IG, SB: No conflicts of interest. VS: advisor/lecturer for Gilead and Abbvie. HR: No conflicts of interest. He works and manages the Center for Disease Analysis (CDA). CDA has received research funding from Gilead and Abbvie. AH: Receipt of grants/research support: Gilead, Novartis, Co-Chair of Hepatitis B and C Public Policy Association funded by Gilead, Abbvie, BMS. Receipt of honoraria or consultation fees: Gilead, BMS. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Nelson PK, Mathers BM, Cowie B, Hagan H, Des Jarlais D, Horyniak D, et al. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B and hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: results of systematic reviews. Lancet. 2011;378(9791):571–83. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61097-0 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3285467. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cornberg M, Razavi HA, Alberti A, Bernasconi E, Buti M, Cooper C, et al. A systematic review of hepatitis C virus epidemiology in Europe, Canada and Israel. Liver international: official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 2011;31 Suppl 2:30–60. 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02539.x . - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global Health Sector Strategy on viral hepatitis, 2016–2021 2015 [cited 2015 28/10]. Available from: http://www.who.int/hiv/draft-hep-strategy-2016-2021_en.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

