Oncologic outcomes after robot-assisted versus laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy: Analysis of the National Cancer Database
- PMID: 30114321
- PMCID: PMC6386178
- DOI: 10.1002/jso.25170
Oncologic outcomes after robot-assisted versus laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy: Analysis of the National Cancer Database
Abstract
Background: How the oncologic outcomes after robotic distal pancreatectomy (RDP) compare to those after laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy (LDP) remains unknown.
Methods: Using the National Cancer Database (NCDB), we analyzed all patients undergoing LDP or RDP for resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma over a 4-year period (2010-2013).
Results: Of the 704 eligible patients, 605 (86%) underwent LDP and 99 (14%) underwent RDP. The median follow-up for patients was 25 months. There were no differences in the two groups with respect to sociodemographic, clinicopathologic, or treatment characteristics. On comparing LDP versus RDP, there was no difference in the margin-positive rate (15% vs 16%; P = 0.84); lymph nodes examined (12 vs 11; P = 0.67); overall survival (hazard ratio [HR], 1.1, 95% confidence intervals [CI], 0.7 to 1.7; 28 vs 25 months; P = 0.71); hospital stay (6 vs 5 days; P = 0.14); time to chemotherapy (50 vs 52 days; P = 0.65); 30-day readmission (9.4% vs 9.1%; P = 0.92); and mortality (1% vs 0%; P = 0.28). Patients undergoing LDP had a significantly higher conversion rate to open or minimally invasive pancreatic cancer resections compared with RDP (27% vs 10%; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The early national experience with RDP demonstrates similar oncologic outcomes to LDP, with a significantly lower conversion rate.
Keywords: laparoscopy; minimally invasive surgery; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; pancreatic resection; robotic surgery.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interest
Figures
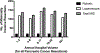

References
-
- Butturini G, Damoli I, Crepaz L, et al. A prospective non-randomised single-center study comparing laparoscopic and robotic distal pancreatectomy. Surg Endosc 2015; 29(11):3163–70. - PubMed
-
- Daouadi M, Zureikat AH, Zenati MS, et al. Robot-assisted minimally invasive distal pancreatectomy is superior to the laparoscopic technique. Ann Surg 2013; 257(1):128–32. - PubMed
-
- Abu Hilal M, Hamdan M, Di Fabio F, et al. Laparoscopic versus open distal pancreatectomy: a clinical and cost-effectiveness study. Surg Endosc 2012; 26(6):1670–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

