Robotic (super) microsurgery: Feasibility of a new master-slave platform in an in vivo animal model and future directions
- PMID: 30114335
- PMCID: PMC6221079
- DOI: 10.1002/jso.25195
Robotic (super) microsurgery: Feasibility of a new master-slave platform in an in vivo animal model and future directions
Abstract
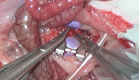
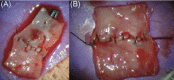
Advanced microsurgical procedures are currently limited by human precision and manual dexterity. The potential of robotics in microsurgery is highlighted, including a general overview of applications of robotic assistance in microsurgery and its introduction in different surgical specialties. A new robotic platform especially designed for (super) microsurgery is presented. Results of an in vivo animal study underline its feasibility and encourage further development toward clinical studies. Future directions of robotic microsurgery are proposed.
Keywords: microsurgery; robotic surgery.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Surgical Oncology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Selber J. Robotic surgery. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2012;28:433‐434. - PubMed
-
- Park YM, Kim HR, Cho BC, Keum KC, Cho NH, Kim SH. Transoral robotic surgery‐based therapy in patients with stage III‐IV oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2017;75:16‐21. - PubMed
-
- Katz RD, Rosson GD, Taylor JA, Singh NK. Robotics in microsurgery: use of a surgical robot to perform a free flap in a pig. Microsurgery. 2005;25:566‐569. - PubMed
-
- Katz RD, Taylor JA, Rosson GD, Brown PR, Singh NK. Robotics in plastic and reconstructive surgery: use of a telemanipulator slave robot to perform microvascular anastomoses. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2006;22:53‐57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

