MRI-based treatment planning for brain stereotactic radiosurgery: Dosimetric validation of a learning-based pseudo-CT generation method
- PMID: 30115539
- PMCID: PMC7775641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.meddos.2018.06.008
MRI-based treatment planning for brain stereotactic radiosurgery: Dosimetric validation of a learning-based pseudo-CT generation method
Abstract
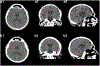
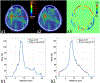
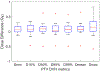
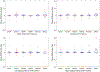
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-only radiotherapy treatment planning is attractive since MRI provides superior soft tissue contrast without ionizing radiation compared with computed tomography (CT). However, it requires the generation of pseudo CT from MRI images for patient setup and dose calculation. Our machine-learning-based method to generate pseudo CT images has been shown to provide pseudo CT images with excellent image quality, while its dose calculation accuracy remains an open question. In this study, we aim to investigate the accuracy of dose calculation in brain frameless stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) using pseudo CT images which are generated from MRI images using the machine learning-based method developed by our group. We retrospectively investigated a total of 19 treatment plans from 14 patients, each of whom has CT simulation and MRI images acquired during pretreatment. The dose distributions of the same treatment plans were calculated on original CT simulation images as ground truth, as well as on pseudo CT images generated from MRI images. Clinically-relevant DVH metrics and gamma analysis were extracted from both ground truth and pseudo CT results for comparison and evaluation. The side-by-side comparisons on image quality and dose distributions demonstrated very good agreement of image contrast and calculated dose between pseudo CT and original CT. The average differences in Dose-volume histogram (DVH) metrics for Planning target volume (PTVs) were less than 0.6%, and no differences in those for organs at risk at a significance level of 0.05. The average pass rate of gamma analysis was 99%. These quantitative results strongly indicate that the pseudo CT images created from MRI images using our proposed machine learning method are accurate enough to replace current CT simulation images for dose calculation in brain SRS treatment. This study also demonstrates the great potential for MRI to completely replace CT scans in the process of simulation and treatment planning.
Keywords: MRI; Pseudo CT; Treatment planning.
Copyright © 2018 American Association of Medical Dosimetrists. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dose evaluation of MRI-based synthetic CT generated using a machine learning method for prostate cancer radiotherapy.Med Dosim. 2019 Winter;44(4):e64-e70. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Med Dosim. 2019. PMID: 30713000 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric study on learning-based cone-beam CT correction in adaptive radiation therapy.Med Dosim. 2019 Winter;44(4):e71-e79. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Med Dosim. 2019. PMID: 30948341 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Hounsfield unit assignment and dose differences between CT-based standard and deep learning-based synthetic CT images for MRI-only radiation therapy of the head and neck.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jan;25(1):e14239. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14239. Epub 2023 Dec 21. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38128040 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in synthetic CT generation from MRI: A review of techniques, and trends in radiation therapy planning.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Nov;25(11):e14499. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14499. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39325781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging for brain stereotactic radiotherapy : A review of requirements and pitfalls.Strahlenther Onkol. 2020 May;196(5):444-456. doi: 10.1007/s00066-020-01604-0. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Strahlenther Onkol. 2020. PMID: 32206842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep learning-based image quality improvement for low-dose computed tomography simulation in radiation therapy.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2019 Oct;6(4):043504. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.6.4.043504. Epub 2019 Oct 24. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2019. PMID: 31673567 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Tumor Segmentation Based on Hybrid Clustering and Morphological Operations.Int J Biomed Imaging. 2019 Apr 9;2019:7305832. doi: 10.1155/2019/7305832. eCollection 2019. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31093268 Free PMC article.
-
Image-Guided Proton Therapy: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;15(9):2555. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092555. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37174022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning in medical image registration: a review.Phys Med Biol. 2020 Oct 22;65(20):20TR01. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab843e. Phys Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32217829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feasibility of artificial-intelligence-based synthetic computed tomography in a magnetic resonance-only radiotherapy workflow for brain radiotherapy: Two-way dose validation and 2D/2D kV-image-based positioning.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2022 Oct 22;24:111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2022.10.002. eCollection 2022 Oct. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36405564 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

