Lycopene ameliorates oxidative stress in the aging chicken ovary via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
- PMID: 30115814
- PMCID: PMC6128425
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.101526
Lycopene ameliorates oxidative stress in the aging chicken ovary via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
Abstract
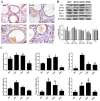
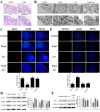
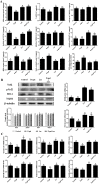
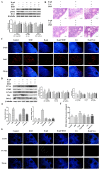
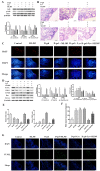
After 480 days of age, high-producing hens are likely to be subject to ovarian aging, mainly due to oxidative stress. In this study, the amelioration of ovarian aging in chickens, using a plant antioxidant, lycopene, was investigated. The activity of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in chicken ovaries at different ages (90, 150, 280 and 580 days old) were compared to elucidate any age-related changes. Subsequently, the putative attenuating effect of lycopene (100 ng/mL) on ovarian aging was evaluated through the establishment of a D-gal-induced aging ovarian culture model. The cultured ovarian tissues of young (280 days) and old (580 days) hens were treated with lycopene for 72 h to verify protective effects of lycopene on naturally aged ovaries. Results showed that the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway was down-regulated during the ovarian aging process. Lycopene rescued the decreased antioxidant capacity by increasing the activities of antioxidases and activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in both D-gal-induced and naturally aged ovaries. Moreover, lycopene promoted cell proliferation and inhibited apoptosis in both D-gal-induced and naturally aged ovaries. Lycopene also alleviated D-gal-induced mitochondrial damage in the living granulosa cells. In conclusion, lycopene can effectively ameliorate the oxidative stress in aging hen ovaries via the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Keywords: Nrf2/HO-1; chicken; lycopene,ovarian aging; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ben-Meir A, Burstein E, Borrego-Alvarez A, Chong J, Wong E, Yavorska T, Naranian T, Chi M, Wang Y, Bentov Y, Alexis J, Meriano J, Sung HK, et al.. Coenzyme Q10 restores oocyte mitochondrial function and fertility during reproductive aging. Aging Cell. 2015; 14:887–95. 10.1111/acel.12368 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

