A Comet Assay for DNA Damage and Repair After Exposure to Carbon-Ion Beams or X-rays in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
- PMID: 30116170
- PMCID: PMC6088507
- DOI: 10.1177/1559325818792467
A Comet Assay for DNA Damage and Repair After Exposure to Carbon-Ion Beams or X-rays in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
Abstract
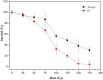
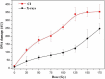
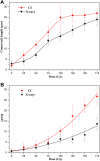
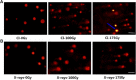
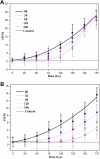
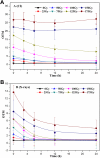
Ionizing radiation (IR) can result in serious genomic instability and genotoxicity by causing DNA damage. Carbon ion (CI) beams and X-rays are typical IRs and possess high-linear energy transfer (LET) and low-LET, respectively. In this article, a comet assay that was optimized by decreasing the electrophoresis time (8 minutes) and voltage (0.5 V/cm) was performed to elucidate and quantify the DNA damage induced by CI or X-rays radiation. Two quantitative methods for the comet assay, namely, comet score and olive tail moment, were compared, and the appropriate means and parameter values were selected for the present assay. The dose-effect relationship for CI or X-rays radiation and the DNA repair process were studied in yeast cells. These results showed that the quadratic function fitted the dose-effect relationship after CI or X-rays exposure, and the trend for the models fitted the dose-effect curves for various repair times was precisely described by the cubic function. A kinetics model was also creatively used to describe the process of DNA repair, and equations were calculated within repairable ranges that could be used to roughly evaluate the process and time necessary for DNA repair.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA repair; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; comet assay; model fitting.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Measurement of the initial levels of DNA damage in human lymphocytes induced by 29 kV X rays (mammography X rays) relative to 220 kV X rays and gamma rays.Radiat Res. 2005 May;163(5):510-9. doi: 10.1667/rr3343. Radiat Res. 2005. PMID: 15850412
-
Evaluation of the effect of 90Sr beta-radiation on human blood cells by chromosome aberration and single cell gel electrophoresis (comet assay) analysis.Mutat Res. 2001 May 9;476(1-2):109-21. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00100-2. Mutat Res. 2001. PMID: 11336988
-
Evaluation of γ-radiation-induced DNA damage in two species of bivalves and their relative sensitivity using comet assay.Aquat Toxicol. 2014 May;150:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.02.007. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Aquat Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24642292
-
Measuring oxidative DNA damage and DNA repair using the yeast comet assay.Yeast. 2011 Jan;28(1):55-61. doi: 10.1002/yea.1820. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Yeast. 2011. PMID: 20824890
-
Genotoxicity of environmental agents assessed by the alkaline comet assay.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;96 Suppl 1:1-42. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15859009 Review.
Cited by
-
Dna2 removes toxic ssDNA-RPA filaments generated from meiotic recombination-associated DNA synthesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Aug 25;51(15):7914-7935. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad537. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37351599 Free PMC article.
-
Furfural tolerance of mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae selected via ionizing radiation combined with adaptive laboratory evolution.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024 Aug 22;17(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02562-w. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024. PMID: 39175057 Free PMC article.
-
Ku70 affects the frequency of chromosome translocation in human lymphocytes after radiation and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Radiat Oncol. 2022 Aug 19;17(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02113-3. Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35986335 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring Biochemical Changes of Neuroblastoma Cells in Early Stages After X-Ray Exposure by Using Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Nov 22;24(23):7459. doi: 10.3390/s24237459. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39685995 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro assays for investigating the FLASH effect.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022 Feb 28;24:e10. doi: 10.1017/erm.2022.5. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35225211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pouget JP, Douki T, Richard MJ, Cadet J. DNA damage induced in cells by γ and UVA radiation as measured by HPLC/GC-MS and HPLC-EC and comet assay. Chem Res Toxicol. 2000;13(7):541–549. - PubMed
-
- Ohnishi T, Mori E, Takahashi A. DNA double-strand breaks: their production, recognition, and repair in eukaryotes. Mutat Res. 2009;669(1-2):8–12. - PubMed
-
- Hirano T, Kazama Y, Ohbu S, et al. Molecular nature of mutations induced by high-LET irradiation with argon and carbon ions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen. 2012;735(1-2):19–31. - PubMed
-
- Mcmahon SJ, Currell FJ. A robust curve-fitting procedure for the analysis of plasmid DNA strand break data from gel electrophoresis. Radiat Res. 2011;175(6):797–805. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

