Inhibitory Effect of Anoectochilus formosanus Extract on Hyperglycemia-Related PD-L1 Expression and Cancer Proliferation
- PMID: 30116189
- PMCID: PMC6082959
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00807
Inhibitory Effect of Anoectochilus formosanus Extract on Hyperglycemia-Related PD-L1 Expression and Cancer Proliferation
Abstract
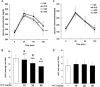
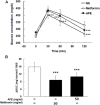
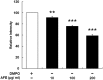
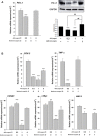
Traditional herb medicine, golden thread (Anoectochilus formosanus Hayata) has been used to treat various diseases. Hyperglycemia induces generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhancement of oxidative stress which are risk factors for cancer progression and metastasis. In this study, we evaluated hypoglycemic effect of A. formosanus extracts (AFEs) in an inducible hyperglycemia animal model and its capacity of free-radical scavenging to establish hyperglycemia-related carcinogenesis. AFE reduced blood glucose in hyperglycemic mice while there was no change in control group. The incremental area under blood glucose response curve was decreased significantly in hyperglycemic mice treated with AFE in a dose-dependent manner. AFE and metformin at the same administrated dose of 50 mg/kg showed similar effect on intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test in hyperglycemic mice. Free-radical scavenger capacity of AFE was concentration dependent and 200 μg/ml of AFE was able to reduce more than 41% of the free radical. Treatment of cancer cells with AFE inhibited constitutive PD-L1 expression and its protein accumulation. It also induced expression of pro-apoptotic genes but inhibited proliferative and metastatic genes. In addition, it induced anti-proliferation in cancer cells. The results suggested that AFE not only reduced blood glucose concentration as metformin but also showed its potential use in cancer immune chemoprevention/therapy via hypoglycemic effect, ROS scavenging and PD-L1 suppression.
Keywords: PD-L1; anti-proliferation; cancer; hyperglycemia; metformin.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Scavenging of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of the oxidation of low density lipoprotein by the aqueous extraction of Anoectochilus formosanus.Am J Chin Med. 2003;31(1):25-36. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X03000692. Am J Chin Med. 2003. PMID: 12723752
-
Antihyperglycaemic and anti-oxidant properties of Anoectochilus formosanus in diabetic rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002 Aug;29(8):684-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2002.03717.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12100000
-
Radical scavenging-linked anti-adipogenic activity of Alnus firma extracts.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jan;41(1):119-128. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3221. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29115568 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal Medicines Attenuate PD-L1 Expression to Induce Anti-Proliferation in Obesity-Related Cancers.Nutrients. 2019 Dec 5;11(12):2979. doi: 10.3390/nu11122979. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31817534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of PD-L1 expression on cancer cells with ROS-modulating drugs.Life Sci. 2020 Apr 1;246:117403. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117403. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32035131 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Effect of Anoectochilus formosanus Polysaccharide against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression in BALB/c Mice.Foods. 2023 May 7;12(9):1910. doi: 10.3390/foods12091910. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37174447 Free PMC article.
-
Orchidaceae-Derived Anticancer Agents: A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 31;14(3):754. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030754. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35159021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges Coexist with Opportunities: Spatial Heterogeneity Expression of PD-L1 in Cancer Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jan;11(1):e2303175. doi: 10.1002/advs.202303175. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 37934012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin as an archetype immuno-metabolic adjuvant for cancer immunotherapy.Oncoimmunology. 2019 Jun 25;8(10):e1633235. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1633235. eCollection 2019. Oncoimmunology. 2019. PMID: 31646077 Free PMC article.
-
LED Lights Promote Growth and Flavonoid Accumulation of Anoectochilus roxburghii and Are Linked to the Enhanced Expression of Several Related Genes.Plants (Basel). 2020 Oct 12;9(10):1344. doi: 10.3390/plants9101344. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33053736 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

