Resistance-Trained Individuals Are Less Susceptible to Oxidative Damage after Eccentric Exercise
- PMID: 30116488
- PMCID: PMC6079342
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6857190
Resistance-Trained Individuals Are Less Susceptible to Oxidative Damage after Eccentric Exercise
Abstract
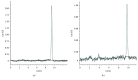
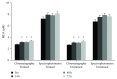
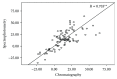
It has been proposed that exercise-induced oxidative stress and adaptations are dependent on training status. In this study, we examined the effects of training background on free radical generation and adaptations after eccentric exercise. Forty volunteers were divided into two groups (trained and untrained) and were asked to perform eccentric exercise. Then, their blood samples were collected pre, 24, 48, and 72 hours postexercise. Biomarkers indicating oxidative damage and the antioxidant profiles of the participants were measured in plasma and erythrocyte lysate both spectrophotometrically and chromatographically. The results revealed that the untrained group depicted more severe oxidative damage (protein carbonyls, malondialdehyde), weaker antioxidant status (reduced glutathione, static and capacity oxidation-reduction potential), and weaker radical-scavenging activity (superoxide radical scavenging and reducing power) compared to the trained participants. Our findings show that trained individuals are less susceptible to oxidative damage and suggest that generalized nutritional recommendations regarding recovery after exercise should be avoided.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endurance training attenuates exercise-induced oxidative stress in erythrocytes in rat.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2004 May;91(5-6):622-7. doi: 10.1007/s00421-003-1029-6. Epub 2003 Dec 18. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14685869
-
Endurance training attenuates the oxidative stress due to acute exhaustive exercise in rat liver.Acta Physiol Hung. 2008 Dec;95(4):337-47. doi: 10.1556/APhysiol.95.2008.4.2. Acta Physiol Hung. 2008. PMID: 19009910
-
Altered oxidative stress in overtrained athletes.J Sports Sci. 2010 Feb;28(3):309-17. doi: 10.1080/02640410903473844. J Sports Sci. 2010. PMID: 20077275 Clinical Trial.
-
The role of antioxidant vitamins and enzymes in the prevention of exercise-induced muscle damage.Sports Med. 1996 Mar;21(3):213-38. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199621030-00005. Sports Med. 1996. PMID: 8776010 Review.
-
Antioxidants: what role do they play in physical activity and health?Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Aug;72(2 Suppl):637S-46S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/72.2.637S. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000. PMID: 10919970 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Antioxidant and Antimutagenic Properties of Red and White Wine Extracts In Vitro.Metabolites. 2021 Jul 2;11(7):436. doi: 10.3390/metabo11070436. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34357330 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of eccentric exercise on different slopes.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2019 Dec 1;19(4):412-421. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2019. PMID: 31789292 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Different Exercise Modalities on Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 11;2021:1947928. doi: 10.1155/2021/1947928. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33628774 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Baduanjin exercise on cognitive frailty, oxidative stress, and chronic inflammation in older adults with cognitive frailty: a randomized controlled trial.Front Public Health. 2024 May 23;12:1385542. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1385542. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38846613 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Supplementation with Vitamins C and E and Exercise-Induced Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness: A Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 12;10(2):279. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020279. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673055 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Serravite D. H., Perry A., Jacobs K. A., Adams J. A., Harriell K., Signorile J. F. Effect of whole-body periodic acceleration on exercise-induced muscle damage after eccentric exercise. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance. 2014;9(6):985–992. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2013-0512. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brentano M. A., Martins Kruel L. F. A review on strength exercise-induced muscle damage: applications, adaptation mechanisms and limitations. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness. 2011;51(1):1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

