Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Maxillary Sinuses Inflammatory Diseases: Report of Three Cases and Literature Review
- PMID: 30116516
- PMCID: PMC6090247
- DOI: 10.5037/jomr.2018.9204
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Maxillary Sinuses Inflammatory Diseases: Report of Three Cases and Literature Review
Abstract
Background: Magnetic resonance imaging is considered a preferable imaging examination in the diagnosis of inflammatory maxillary sinus disease and can provide precise sinonasal characterization. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient are complementary magnetic resonance imaging tools that can be applied to the differentiation of sinus diseases. In this report, 3 cases of inflammatory maxillary sinus diseases imaging findings considering diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging features were described. Additionally, a literature review considering the use of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in inflammatory lesions is provided.
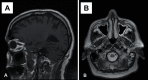
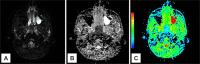
Methods: The cases reported were: presence of air-fluid levels, mucosal thickening and a mucous retention cyst. Conventional magnetic resonance imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps, with ADC values were demonstrated. In the literature review, the studies considering inflammatory lesions were detailed, as well as ADC values established by investigators.
Results: ADC values for presence of air-fluid levels, mucosal thickening and mucous retention cyst were respectively: 1.99 x 10-3 mm2/s; 1.83 x 10-3 mm2/s; 2.05 x 10-3 mm2/s.
Conclusions: It was observed that apparent diffusion coefficient values from the inflammatory lesions described in this report were different and apparent diffusion coefficient may be useful in the differentiation of these maxillary sinus alterations. Further larger sample investigations considering apparent diffusion coefficient values focusing in inflammatory lesions are recommended. The lack of studies considering the use of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging on inflammatory diseases diagnostic was the major limitation to the literature review.
Keywords: inflammatory disease; magnetic resonance imaging; maxillary sinus; paranasal sinuses.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The value of the apparent diffusion coefficient calculated from diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scans in the differentiation of maxillary sinus inflammatory diseases.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2019 May;127(5):433-443. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2018.11.013. Epub 2018 Dec 1. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30600171
-
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the paranasal sinuses: A systematic review.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2018 Dec;126(6):521-536. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30143461
-
Evaluation of the efficacy of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and apparent diffusion coefficients in the diagnosis of maxillary diseases.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2023 Dec;136(6):753-758. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2023.06.012. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37517952
-
Correlation of quantitative MR imaging findings with symptoms in patients with incidentally detected inflammatory sinonasal disease.Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018 Feb;99(2):65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2017.05.012. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018. PMID: 28729182
-
Magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging: extraneurological applications.Radiol Med. 2006 Apr;111(3):392-419. doi: 10.1007/s11547-006-0037-0. Epub 2006 Apr 11. Radiol Med. 2006. PMID: 16683086 Review. English, Italian.
Cited by
-
Imaging technologies for the detection of sinus pathologies of odontogenic origin. A review.Rev Cient Odontol (Lima). 2021 Mar 11;9(1):e049. doi: 10.21142/2523-2754-0901-2021-049. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. Rev Cient Odontol (Lima). 2021. PMID: 38464402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of mandibular bone marrow: do apparent diffusion coefficient values of the cervical vertebrae and mandible correlate with age?Oral Radiol. 2022 Jan;38(1):72-79. doi: 10.1007/s11282-021-00528-4. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Oral Radiol. 2022. PMID: 33877509
-
Visualization of clinically silent, odontogenic maxillary sinus mucositis originating from periapical inflammation using MRI: a feasibility study.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Jul;27(7):3705-3712. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-04986-4. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 37039958 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based multimodal MRI texture analysis for assessing renal function and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy: a retrospective study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 17;14:1050078. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1050078. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37139339 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of CGRP distributions in the maxillary sinus and trigeminal ganglion between elderly dentulous and edentulous humans.Eur J Histochem. 2021 Mar 31;65(2):3234. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2021.3234. Eur J Histochem. 2021. PMID: 33787056 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
