Soluble Guanylate Cyclase As the Key Enzyme in the Modulating Effect of NO on Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
- PMID: 30116618
- PMCID: PMC6087819
Soluble Guanylate Cyclase As the Key Enzyme in the Modulating Effect of NO on Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors
Abstract
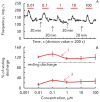
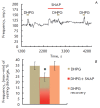
The synaptic plasticity of the afferent synapse of the vestibular apparatus is defined by the dynamic interaction of ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors and the modulators of synaptic transmission. It was shown that nitric oxide modulates iGluR responses. In this paper, the effect of NO on the function of the afferent synapse mGluR was investigated. Inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase lowered the level of background activity but increased the amplitude of the responses of groups I and II mGluR agonist ACPD. Donor NO SNAP increased the level of background activity. Short-term perfusion of the synaptic region with low concentrations of SNAP led to a decrease in the amplitude of the answers of mGluR agonists ACPD and DHPG. The inhibitory effect of the NO donor was eliminated under blockade of soluble guanylate cyclase with a specific inhibitor ODQ. A prolonged application of NO did not cause a statistically significant change in the amplitude of the ACPD response. However, SNAP at concentrations of 10 and 100 μM increased the amplitude of the mGluR agonist responses 30 and 15 minutes, respectively, after termination of the NO donor exposure. The obtained data show the multidirectional effect of NO on the function of mGluR and testify to the existence of a complex modulating mechanism of the afferent flow from vestibular organs to the central nervous system.
Keywords: metabotropic glutamate receptors; nitric oxide; soluble guanylate cyclase; synaptic plasticity; vestibular apparatus.
Figures



References
-
- Flores A., Leyn-Olea M., Vega R., Soto E.. Neurosci. Lett. 1996;205:131–134. - PubMed
-
- Takumida M., Anniko M.. In vivo. 2004;18:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Takumida M., Anniko M.. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 1998;60:67–72. - PubMed
-
- a. Popa R., Anniko M., Takumida M.. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000;120:350–358. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
