Factors Affecting the Absorption of Subcutaneously Administered Insulin: Effect on Variability
- PMID: 30116732
- PMCID: PMC6079517
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1205121
Factors Affecting the Absorption of Subcutaneously Administered Insulin: Effect on Variability
Abstract
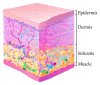
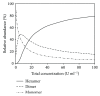
Variability in the effect of subcutaneously administered insulin represents a major challenge in insulin therapy where precise dosing is required in order to achieve targeted glucose levels. Since this variability is largely influenced by the absorption of insulin, a deeper understanding of the factors affecting the absorption of insulin from the subcutaneous tissue is necessary in order to improve glycaemic control and the long-term prognosis in people with diabetes. These factors can be related to either the insulin preparation, the injection site/patient, or the injection technique. This review highlights the factors affecting insulin absorption with special attention on the physiological factors at the injection site. In addition, it also provides a detailed description of the insulin absorption process and the various modifications to this process that have been utilized by the different insulin preparations available.
Figures
References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine. 1993;329(14):977–986. doi: 10.1056/nejm199309303291401. - DOI - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33) The Lancet. 1998;352(9131):837–853. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)07019-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

