EUS-guided portal pressure measurement (with videos)
- PMID: 30117489
- PMCID: PMC6106144
- DOI: 10.4103/eus.eus_35_18
EUS-guided portal pressure measurement (with videos)
Abstract
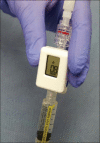
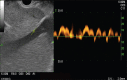
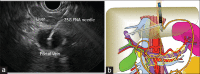
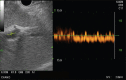
A growing number of studies have explored EUS-guided vascular catheterization due to the relative proximity of the gastrointestinal tract to the major blood vessels of the mediastinum and abdomen. In particular, EUS-guided access of the portal vein (PV) may be favorable given the relative difficulty of PV access through standard percutaneous routes. Two major diagnostic applications of EUS-guided vascular access include angiography and assessment of intravascular pressure. This review will outline the different devices and techniques employed to obtain angiographic visualization and/or direct pressure measurements of the portal circulation. Ease of access, safety, and important lessons learned from each approach will be highlighted.
Keywords: EUS; hepatic venous portal gradient; portal vein angiography; portal vein manometry; portal venous pressure.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures


References
-
- Lai L, Poneros J, Santilli J, et al. EUS-guided portal vein catheterization and pressure measurement in an animal model: A pilot study of feasibility. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:280–3. - PubMed
-
- Magno P, Ko CW, Buscaglia JM, et al. EUS-guided angiography: A novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the vascular system. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:587–91. - PubMed
-
- Giday SA, Ko CW, Clarke JO, et al. EUS-guided portal vein carbon dioxide angiography: A pilot study in a porcine model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:814–9. - PubMed
-
- Giday SA, Clarke JO, Buscaglia JM, et al. EUS-guided portal vein catheterization: A promising novel approach for portal angiography and portal vein pressure measurements. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:338–42. - PubMed
-
- Brugge WR. EUS is an important new tool for accessing the portal vein. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:343–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

