Epigenetic silenced miR-125a-5p could be self-activated through targeting Suv39H1 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 30117667
- PMCID: PMC6156292
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13716
Epigenetic silenced miR-125a-5p could be self-activated through targeting Suv39H1 in gastric cancer
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Epigenetic silenced miR-125a-5p could be self-activated through targeting Suv39H1 in gastric cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Feb;25(4):2285. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15847. Epub 2021 Jan 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33586364 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
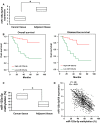
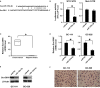
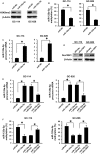
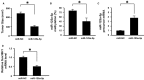
Emerging evidence suggests that microRNAs (miRNAs) serve an important role in tumorigenesis and development. Although the low expression of miR-125a-5p in gastric cancer has been reported, the underlying mechanism remains unknown. In the current study, the low expression of miR-125a-5p in gastric cancer was verified in paired cancer tissues and adjacent non-tumour tissues. Furthermore, the GC islands in the miR-125a-5p region were hypermethylated in the tumour tissues. And the hypermethylation was negatively correlated with the miR-125a-5p expression. Target gene screening showed that the histone methyltransferase Suv39H1 was one of the potential target genes. In vitro studies showed that miR-125a-5p could directly suppress the Suv39H1 expression and decrease the H3K9me3 levels. On the other hand, the Suv39H1 could induce demethylation of miR-125a-5p, resulting in re-activation of miR-125a-5p. What is more, overexpessing miR-125a-5p could also self-activate the silenced miR-125a-5p in gastric cancer cells, which suppressed cell migration, invasion and proliferation in vitro and inhibited cancer progression in vivo. Thus, we uncovered here that the epigenetic silenced miR-125a-5p could be self-activated through targeting Suv39H1 in gastric cancer, suggesting that miR-125a-5p might be not only the potential prognostic value as a tumour biomarker but also potential therapeutic targets in gastric cancer.
Keywords: Suv39H1; epigenetic silence; gastric cancer; miR-125a-5p.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Shen L, Shan YS, HU HM, et al. Management of gastric cancer in Asia: resource‐stratified guidelines. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:e535‐e547. - PubMed
-
- Varadhachary G, Ajani JA. Gastric cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2005;3:118‐124. - PubMed
-
- Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH, et al. MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: a new player enters the game. Oncogene. 2010;29:5761‐5771. - PubMed
-
- Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:203‐222. - PubMed
-
- Bracken CP, Scott HS, Goodall GJ. A network‐biology perspective of microRNA function and dysfunction in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:719‐732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

