Mixed Meal and Intravenous L-Arginine Tests Both Stimulate Incretin Release Across Glucose Tolerance in Man: Lack of Correlation with β Cell Function
- PMID: 30117761
- PMCID: PMC6167614
- DOI: 10.1089/met.2018.0022
Mixed Meal and Intravenous L-Arginine Tests Both Stimulate Incretin Release Across Glucose Tolerance in Man: Lack of Correlation with β Cell Function
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Mixed Meal and Intravenous L-Arginine Tests Both Stimulate Incretin Release Across Glucose Tolerance in Man: Lack of Correlation with β Cell Function by Ruetten H, MD, PhD, Gebauer M, PhD, Raymond RH, MS, Calle RA, MD, Cobelli C, PhD, Ghosh A, PhD, Robertson RP, MD, Shankar SS, MD, Staten MA, MD, Stefanovski D, PhD, Vella A, MD, Wright K, MS, and Fryburg DA, MD; on behalf of the Foundation for the NIH Biomarkers Consortium Beta Cell Project Team Metab Syndr Relat Disord 2018;16:406-415 DOI 10.1089/met.2018.0022.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2019 Mar;17(2):128. doi: 10.1089/met.2018.0022.correx. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 30822261 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
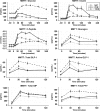
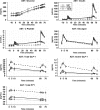
Background: The aims of this study were to 1. define the responses of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), glucagon, and peptide YY (PYY) to an oral meal and to intravenous L-arginine; and 2. examine correlation of enteroendocrine hormones with insulin secretion. We hypothesized a relationship between circulating incretin concentrations and insulin secretion.
Methods: Subjects with normal glucose tolerance (NGT, n = 23), prediabetes (PDM, n = 17), or with type 2 diabetes (T2DM, n = 22) were studied twice, following a mixed test meal (470 kCal) (mixed meal tolerance test [MMTT]) or intravenous L-arginine (arginine maximal stimulation test [AST], 5 g). GLP-1 (total and active), PYY, GIP, glucagon, and β cell function were measured before and following each stimulus.
Results: Baseline enteroendocrine hormones differed across the glucose tolerance (GT) spectrum, T2DM generally >NGT and PDM. In response to MMTT, total and active GLP-1, GIP, glucagon, and PYY increased in all populations. The incremental area-under-the-curve (0-120 min) of analytes like total GLP-1 were often higher in T2DM compared with NGT and PDM (35-51%; P < 0.05). At baseline glucose, L-arginine increased total and active GLP-1 and glucagon concentrations in all GT populations (all P < 0.05). As expected, the MMTT and AST provoked differential glucose, insulin, and C-peptide responses across GT populations. Baseline or stimulated enteroendocrine hormone concentrations did not consistently correlate with either measure of β cell function.
Conclusions/interpretation: Both MMTT and AST resulted in insulin and enteroendocrine hormone responses across GT populations without consistent correlation between release of incretins and insulin, which is in line with other published research. If a defect is in the enteroendocrine/β cell axis, it is probably reduced response to rather than diminished secretion of enteroendocrine hormones.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01454973 NCT01663207 NCT01663220.
Keywords: GLP-1; arginine; incretin; insulin secretion; meal tolerance test; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
H.R., and M.G., employee and shareholder of Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH. R.A.C., employee and shareholder of Pfizer. A.G., employee and shareholder of Janssen Pharmaceuticals. S.S.S., employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly and Co. D.A.F., shareholder, Pfizer, Inc. For R.H.R., C.C., R.P.R., M.A.S., D.S., A.V., and K.W. no conflicting financial interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Adrian TE, Ferri GL, Bacarese-Hamilton AJ, et al. . Human distribution and release of a putative new gut hormone, peptide YY. Gastroenterology 1985;89:1070–1077 - PubMed
-
- Grandt D, Schimiczek M, Struk K, et al. . Characterization of two forms of peptide YY, PYY(1–36) and PYY(3–36), in the rabbit. Peptides 1994;15:815–820 - PubMed
-
- Hojberg PV, Vilsboll T, Rabol R, et al. . Four weeks of near-normalisation of blood glucose improves the insulin response to glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009;52:199–207 - PubMed
-
- Kjems LL, Holst JJ, Volund A, et al. . The influence of GLP-1 on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: Effects on beta-cell sensitivity in type 2 and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes 2003;52:380–386 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
