Stearoly-CoA desaturase 1 differentiates early and advanced dengue virus infections and determines virus particle infectivity
- PMID: 30118512
- PMCID: PMC6114894
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007261
Stearoly-CoA desaturase 1 differentiates early and advanced dengue virus infections and determines virus particle infectivity
Abstract
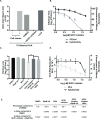
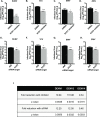
Positive strand RNA viruses, such as dengue virus type 2 (DENV2) expand and structurally alter ER membranes to optimize cellular communication pathways that promote viral replicative needs. These complex rearrangements require significant protein scaffolding as well as changes to the ER chemical composition to support these structures. We have previously shown that the lipid abundance and repertoire of host cells are significantly altered during infection with these viruses. Specifically, enzymes in the lipid biosynthesis pathway such as fatty acid synthase (FAS) are recruited to viral replication sites by interaction with viral proteins and displayed enhanced activities during infection. We have now identified that events downstream of FAS (fatty acid desaturation) are critical for virus replication. In this study we screened enzymes in the unsaturated fatty acid (UFA) biosynthetic pathway and found that the rate-limiting enzyme in monounsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1), is indispensable for DENV2 replication. The enzymatic activity of SCD1, was required for viral genome replication and particle release, and it was regulated in a time-dependent manner with a stringent requirement early during viral infection. As infection progressed, SCD1 protein expression levels were inversely correlated with the concentration of viral dsRNA in the cell. This modulation of SCD1, coinciding with the stage of viral replication, highlighted its function as a trigger of early infection and an enzyme that controlled alternate lipid requirements during early versus advanced infections. Loss of function of this enzyme disrupted structural alterations of assembled viral particles rendering them non-infectious and immature and defective in viral entry. This study identifies the complex involvement of SCD1 in DENV2 infection and demonstrates that these viruses alter ER lipid composition to increase infectivity of the virus particles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Classical swine fever virus utilizes stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1-mediated lipid metabolism to facilitate viral replication.J Virol. 2025 Jun 17;99(6):e0055125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00551-25. Epub 2025 May 19. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40387378 Free PMC article.
-
Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1 (SCD1) regulates foot-and-mouth disease virus replication by modulating host cell lipid metabolism and viral protein 2C-mediated replication complex formation.J Virol. 2024 Oct 22;98(10):e0090224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00902-24. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39324793 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1α Promotes Zika Virus Infection through Regulation of Stearoyl Coenzyme A Desaturase 1-Mediated Lipid Metabolism.J Virol. 2020 Nov 9;94(23):e01229-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01229-20. Print 2020 Nov 9. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32967957 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Role of Phenolic Compounds against Dengue Virus: A Review.Biomolecules. 2020 Dec 24;11(1):11. doi: 10.3390/biom11010011. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33374457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dengue virus and autophagy.Viruses. 2011 Aug;3(8):1332-41. doi: 10.3390/v3081332. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994782 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dengue virus and lipid metabolism: unravelling the interplay for future therapeutic approaches.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2477647. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2477647. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 40059731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dengue virus is particularly sensitive to interference with long-chain fatty acid elongation and desaturation.J Biol Chem. 2025 Mar;301(3):108222. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108222. Epub 2025 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39863099 Free PMC article.
-
Anopheles coluzzii stearoyl-CoA desaturase is essential for adult female survival and reproduction upon blood feeding.PLoS Pathog. 2021 May 20;17(5):e1009486. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009486. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34015060 Free PMC article.
-
Hijacking the Supplies: Metabolism as a Novel Facet of Virus-Host Interaction.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 3;10:1533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01533. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31333664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The circadian clock components BMAL1 and REV-ERBα regulate flavivirus replication.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 22;10(1):377. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08299-7. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30670689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ntambi J. M., Miyazaki M. and Dobrzyn A. (2004) ‘Regulation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase expression.’, Lipids, 39(11), pp. 1061–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

