IL-33 facilitates proliferation of colorectal cancer dependent on COX2/PGE2
- PMID: 30119635
- PMCID: PMC6098640
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0839-7
IL-33 facilitates proliferation of colorectal cancer dependent on COX2/PGE2
Erratum in
-
Correction to: IL-33 facilitates proliferation of colorectal cancer dependent on COX2/PGE2.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jan 17;39(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-1524-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31948467 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-33 (IL-33) participates in various types of diseases including cancers. Previous studies of this cytokine in cancers mainly focused on its regulation on immune responses by which IL-33 modulated cancer progression. The IL-33 triggered signals in cancer cells remain unclear.
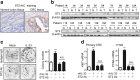
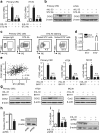
Methods: We analyzed IL-33 gene expression in human colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues and carried out gene enrichment analysis with TCGA Data Portal. We studied CRC proliferation in vivo by inoculating MC38 tumors in IL-33 transgenic mice. We investigated the cell proliferation in vitro with primary CRC cells isolated from fresh human CRC tissues, human CRC cell line HT-29 and mouse CRC cell line MC38. To evaluate the proliferation modulating effects of recombinant IL-33 incubation and other administrated factors, we measured tumor growth, colony formation, cell viability, and the expression of Ki67 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). We used several inhibitors, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) neutralizing antibody, ST2 blocking antibody and specific shRNA expressing plasmid to study the pathway mediating IL-33-induced CRC proliferation. The IL-33 receptor ST2 in human CRC tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry staining and western blotting. The ST2-positive or negative subsets of primary CRC cells were acquired by flow cytometry sorting.
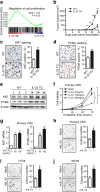
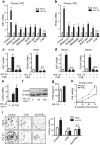
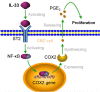
Results: We found that IL-33 expression was correlated with the gene signature of cell proliferation in 394 human CRC samples. The MC38 tumors grew more rapidly and the tumor Ki67 and PCNA were expressed at higher levels in IL-33 transgenic mice than in wild-type mice. IL-33 promoted cell growth, colony formation and expression of Ki67 and PCNA in primary CRC cells as well as CRC cell lines. IL-33 activated cycloxygenase-2 (COX2) expression and increased PGE2 production, whereas the COX2 selective inhibitor and PGE2 neutralizing antibody abolished the proliferation promoting effect of IL-33. ST2 blockade, ST2-negative sorting, NF-κB specific inhibitor and NF-κB specific shRNA (shP65) abrogated the COX2 induction caused by IL-33.
Conclusion: IL-33 facilitates proliferation of colorectal cancer dependent on COX2/PGE2. IL-33 functions via its receptor ST2 and upregulates COX2 expression through NF-κB signaling. Understanding the IL-33 signal transduction in CRC cells provides potential therapeutic targets for clinical treatment.
Keywords: COX2; Colorectal cancer; IL-33; PGE2; Proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experiments with animals and human samples in this study were conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of Tongji Medical College at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Wuhan, Hubei, China).
Consent for publication
All patients signed informed consent for the publication of the clinical images and their clinical details.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23(5):479–490. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.09.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saigusa R, Asano Y, Taniguchi T, Hirabayashi M, Nakamura K, Miura S, Yamashita T, Takahashi T, Ichimura Y, Toyama T, et al. Fli1-haploinsufficient dermal fibroblasts promote skin-localized transdifferentiation of Th2-like regulatory T cells. Arthritis research & therapy. 2018;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1521-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

