A multi-center, double blind randomized controlled trial evaluating flap fixation after mastectomy using sutures or tissue glue versus conventional closure: protocol for the Seroma reduction After Mastectomy (SAM) trial
- PMID: 30119663
- PMCID: PMC6098656
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4740-8
A multi-center, double blind randomized controlled trial evaluating flap fixation after mastectomy using sutures or tissue glue versus conventional closure: protocol for the Seroma reduction After Mastectomy (SAM) trial
Abstract
Background: Seroma formation is a common complication after mastectomy and is associated with delayed wound healing, infection, skin flap necrosis, patient discomfort and repeated visits to the out patient clinic to deal with seroma and its sequelae. Closing the dead space after mastectomy seems to be key in reducing seroma and its complications. Various methods have been described to reduce the dead space after mastectomy: closed suction drainage, quilting of the skin flaps and application of adhesive tissue glues. The aim of this trial is to compare seroma formation and its sequelae in the various methods of flap fixation.
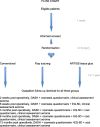
Methods: This is a multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trial in female breast cancer patients undergoing mastectomy, with or without axillary clearance. Exclusion criteria consist of breast conserving therapy, direct breast reconstruction and incapacity to comprehend implications and extent of study and unable to sign for informed consent. A total of 336 patients will be randomized. Patients will be randomly allocated to one of three treatment arms consisting of flap fixation using ARTISS tissue glue with a low suction drain, flap fixation using sutures and a low suction drain or conventional wound closure (without flap fixation) and low suction drainage. Follow up will be conducted up to twelve months post surgery. The primary outcome is the number of seroma aspirations and secondary outcomes consist of number of out patient clinic visits, surgical skin infection rate, shoulder function, cosmesis, health-related quality of life and costs and cost-effectiveness (cost/QALY).
Discussion: This is the first study of its kind to evaluate the effect of flap fixation and its sequelae (ie seroma aspirations, number of out patient clinic visits, infection, shoulder function, patient assessed cosmesis, quality of life and cost-effectiveness) in a double blind randomized controlled trial.
Trial registration: This trial was approved by the hospitals' joint medical ethical committee (14-T-21, 2 June 2014). The SAM Trial is registered in ClinicalTrials.gov since October 2017, Identifier: NCT03305757 .
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness; Flap fixation; Mastectomy; QALY; Quilting; Seroma aspiration; Seroma formation; Shoulder function; Tissue glue.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent will be obtained from all trial participants. This trial was approved by the hospitals’ joint medical ethical committee (
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
-
- Kumar S, et al. Post-mastectomy seroma: a new look into the aetiology of an old problem. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1995;40:292–294. - PubMed
-
- Woodworth PA, et al. Seroma formation after breast cancer surgery; incidence and predicting factors. Am Surg. 2000;66(5):444–450. - PubMed
-
- Tadych K, et al. Postmastectomy seromas and wound drainage. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1987;165(6):483–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical