IFN-γ-response mediator GBP-1 represses human cell proliferation by inhibiting the Hippo signaling transcription factor TEAD
- PMID: 30120107
- PMCID: PMC6156764
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20180123
IFN-γ-response mediator GBP-1 represses human cell proliferation by inhibiting the Hippo signaling transcription factor TEAD
Abstract
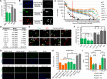
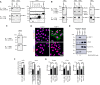
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) is a pleiotropic cytokine that exerts important functions in inflammation, infectious diseases, and cancer. The large GTPase human guanylate-binding protein 1 (GBP-1) is among the most strongly IFN-γ-induced cellular proteins. Previously, it has been shown that GBP-1 mediates manifold cellular responses to IFN-γ including the inhibition of proliferation, spreading, migration, and invasion and through this exerts anti-tumorigenic activity. However, the mechanisms of GBP-1 anti-tumorigenic activities remain poorly understood. Here, we elucidated the molecular mechanism of the human GBP-1-mediated suppression of proliferation by demonstrating for the first time a cross-talk between the anti-tumorigenic IFN-γ and Hippo pathways. The α9-helix of GBP-1 was found to be sufficient to inhibit proliferation. Protein-binding and molecular modeling studies revealed that the α9-helix binds to the DNA-binding domain of the Hippo signaling transcription factor TEA domain protein (TEAD) mediated by the 376VDHLFQK382 sequence at the N-terminus of the GBP-1-α9-helix. Mutation of this sequence resulted in abrogation of both TEAD interaction and suppression of proliferation. Further on, the interaction caused inhibition of TEAD transcriptional activity associated with the down-regulation of TEAD-target genes. In agreement with these results, IFN-γ treatment of the cells also impaired TEAD activity, and this effect was abrogated by siRNA-mediated inhibition of GBP-1 expression. Altogether, this demonstrated that the α9-helix is the proliferation inhibitory domain of GBP-1, which acts independent of the GTPase activity through the inhibition of the Hippo transcription factor TEAD in mediating the anti-proliferative cell response to IFN-γ.
Keywords: cell proliferation; colorectal cancer; guanylate-binding proteins; interferons.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Cheng Y.S., Colonno R.J. and Yin F.H. (1983) Interferon induction of fibroblast proteins with guanylate binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 7746–7750 PMID: - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

