Clinicopathological and Treatment-Associated Prognostic Factors in Patients with Breast Cancer Leptomeningeal Metastases in Relation to Tumor Biology
- PMID: 30120164
- PMCID: PMC6291333
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0200
Clinicopathological and Treatment-Associated Prognostic Factors in Patients with Breast Cancer Leptomeningeal Metastases in Relation to Tumor Biology
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer (BC) is one of the solid tumors most commonly associated with leptomeningeal disease (LMD). LMD carries a devastating prognosis; however, disease presentation and prognostic factors are uncertain.
Subjects, materials, and methods: In order to describe patient characteristics, treatment patterns, and factors associated with survival in a contemporary multicentric cohort, 153 consecutive BC patients diagnosed with LMD at two European institutions (2002-2017) were included. Time to LMD and overall survival (OS) after LMD diagnosis were evaluated using the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards models.
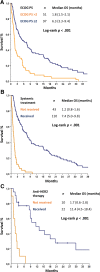
Results: Median age at LMD diagnosis was 58 years (25-84). Tumor phenotype distribution was as follows: hormone receptor (HR) positive (HR+)/human epidermal growth receptor 2 (HER2) negative 51.0%, triple-negative 15.0%, HR+/HER2 positive (HER2+) 13.1% and HR negative/HER2+ 7.2%. Most patients received active anticancer treatments (radiation therapy [RT] n = 42, systemic therapy n = 110, intrathecal treatment n = 103).Median OS was 3.9 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 2.4-5.5). Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) >2, high white blood cells count, low glucose, and high protein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were poor prognostic factors. Having received RT or systemic treatment was associated with better prognosis. In multivariate analysis, ECOG PS (hazard ratio 2.22, 95% CI 1.25-3.94), CSF glucose levels (hazard ratio 1.74, 95% CI 1.05-2.88), and having received systemic treatment (hazard ratio 0.17, 95% CI 0.09-0.32) were confirmed as independent prognostic factors. In HER2+ BC patients, having received systemic HER2-targeted therapy was the only factor maintaining independent prognostication (hazard ratio 0.12, 95% CI 0.02-0.67) in multivariate analysis.
Conclusion: Despite being limited by their retrospective nature, these results highlight the need for clinical trials in BC LMD, stratified on tumor biology.
Implications for practice: Leptomeningeal disease (LMD) is a devastating complication of breast cancer (BC), and its optimal therapy is still not defined. Here, patient characteristics, treatment patterns, and prognostic factors from a contemporary cohort of 153 BC-related LMD patients are reported. In multivariate analysis, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, cerebrospinal fluid glucose levels, and having received systemic treatment were confirmed as independent prognostic factors in the overall population, whereas in human epidermal growth receptor 2 (HER2) positive BC patients, having received systemic HER2-targeted therapy was the only factor maintaining independent prognostication in multivariate analysis. These results highlight the need to consider stratification on tumor biology in the treatment of BC LMD.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Human epidermal growth receptor 2; Leptomeningeal disease; Prognosis; Treatment.
© AlphaMed Press 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Le Rhun E, Weller M, Brandsma D et al. EANO‐ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up of patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumours. Ann Oncol 2017;28:iv84–iv99. - PubMed
-
- Grossman SA, Krabak MJ. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Treat Rev 1999;25:103–119. - PubMed
-
- Le Rhun E, Taillibert S, Zairi F et al. A retrospective case series of 103 consecutive patients with leptomeningeal metastasis and breast cancer. J Neurooncol 2013;113:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Dudani S, Mazzarello S, Hilton J et al. Optimal management of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer patients‐A systematic review. Clin Breast Cancer 2016;16:456–470. - PubMed
-
- Lee YC, Hsieh CC, Chuang JP et al. The necessity of intrathecal chemotherapy for the treatment of breast cancer patients with leptomeningeal metastasis: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Curr Probl Cancer 2017;41:355–370. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

