Insights into degradation mechanism of N-end rule substrates by p62/SQSTM1 autophagy adapter
- PMID: 30120248
- PMCID: PMC6098011
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05825-x
Insights into degradation mechanism of N-end rule substrates by p62/SQSTM1 autophagy adapter
Abstract
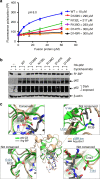
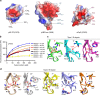
p62/SQSTM1 is the key autophagy adapter protein and the hub of multi-cellular signaling. It was recently reported that autophagy and N-end rule pathways are linked via p62. However, the exact recognition mode of degrading substrates and regulation of p62 in the autophagic pathway remain unknown. Here, we present the complex structures between the ZZ-domain of p62 and various type-1 and type-2 N-degrons. The binding mode employed in the interaction of the ZZ-domain with N-degrons differs from that employed by classic N-recognins. It was also determined that oligomerization via the PB1 domain can control functional affinity to the R-BiP substrate. Unexpectedly, we found that self-oligomerization and disassembly of p62 are pH-dependent. These findings broaden our understanding of the functional repertoire of the N-end rule pathway and provide an insight into the regulation of p62 during the autophagic pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
pH-dependent regulation of SQSTM1/p62 during autophagy.Autophagy. 2019 Jan;15(1):180-181. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1532264. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30290711 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

