Contrast-enhanced photoacoustic imaging in the second near-infrared window using semiconducting polymer nanoparticles
- PMID: 30120826
- PMCID: PMC6975224
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.3.031002
Contrast-enhanced photoacoustic imaging in the second near-infrared window using semiconducting polymer nanoparticles
Abstract
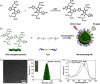
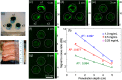
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) is a fast growing deep-tissue imaging modality. However, light scattering and absorption in biological tissues limit imaging depth. Short near-infrared wavelengths (650 to 950 nm) are widely used for PAI. Using longer near-infrared wavelengths reduces scattering. We demonstrate deep-tissue contrast-enhanced in vivo photoacoustic imaging at a wavelength of 1064 nm. An ultranarrow bandgap semiconducting polymer poly (thienoisoindigo-alt-diketopyrrolopyrrole) (denoted as PIGD) is designed and demonstrated for imaging at 1064 nm. By embedding colloidal nanoparticles (NPs) of PIGD in chicken-breast tissue, an imaging depth of ∼5 cm is achieved. Intravenous injection of PIGD NPs in living rats showed brain vascular images with ∼2 times higher contrast compared with the brain vascular images without any contrast agent. Thus, PIGD NPs as an NIR-II contrast agent opens new opportunities for both preclinical and clinical imaging of deep tissues with enhanced contrast.
Keywords: biomaterials; brain vascular imaging; deep-tissue imaging; photoacoustic tomography; second near-infrared window.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Photoacoustic imaging in the second near-infrared window: a review.J Biomed Opt. 2019 Apr;24(4):1-20. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.4.040901. J Biomed Opt. 2019. PMID: 30968648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep tissue photoacoustic imaging of nickel(II) dithiolene-containing polymeric nanoparticles in the second near-infrared window.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 22;10(6):2509-2521. doi: 10.7150/thno.39403. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32194816 Free PMC article.
-
Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles for Centimeters-Deep Photoacoustic Imaging in the Second Near-Infrared Window.Adv Mater. 2017 Nov;29(41). doi: 10.1002/adma.201703403. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Adv Mater. 2017. PMID: 28922476
-
Organic Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles for Photoacoustic Labeling and Tracking of Stem Cells in the Second Near-Infrared Window.ACS Nano. 2018 Dec 26;12(12):12201-12211. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05906. Epub 2018 Nov 21. ACS Nano. 2018. PMID: 30433761
-
Nanomaterials for photoacoustic imaging in the second near-infrared window.Biomater Sci. 2019 Jan 29;7(2):472-479. doi: 10.1039/c8bm00642c. Biomater Sci. 2019. PMID: 30255873 Review.
Cited by
-
Photoacoustic imaging in the second near-infrared window: a review.J Biomed Opt. 2019 Apr;24(4):1-20. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.4.040901. J Biomed Opt. 2019. PMID: 30968648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo 3D Imaging of Retinal Neovascularization Using Multimodal Photoacoustic Microscopy and Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging.J Imaging. 2018 Dec;4(12):150. doi: 10.3390/jimaging4120150. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Imaging. 2018. PMID: 31681820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taruttis A., Ntziachristos V., “Advances in real-time multispectral optoacoustic imaging and its applications,” Nat. Photonics 9(4), 219–227 (2015).10.1038/nphoton.2015.29 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

