Correlation of spectral domain optical coherence tomography with histology and electron microscopy in the porcine retina
- PMID: 30120928
- PMCID: PMC6348113
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.08.003
Correlation of spectral domain optical coherence tomography with histology and electron microscopy in the porcine retina
Abstract
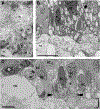
Spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) is used as a non-invasive tool for retinal morphological assessment in vivo. Information on the correlation of SD-OCT with retinal histology in the porcine retina, a model resembling the human retina, is limited. Herein, we correlated the hypo- and hyper-reflective bands on SD-OCT with histology of the lamellar architecture and cellular constituents of the porcine retina. SD-OCT images were acquired with the Heidelberg Spectralis HRA + OCT. Histological analysis was performed using epoxy resin embedded tissue and transmission electron microscopy. Photomicrographs from the histologic sections were linearly scaled to correct for tissue shrinkage and correlated with SD-OCT images. SD-OCT images correlated well with histomorphometric data. A hyper-reflective band in the mid-to-outer inner nuclear layer correlated with the presence of abundant mitochondria in horizontal cell processes and adjacent bipolar cells. A concentration of cone nuclei corresponded to a relative hypo-reflective band in the outer portion of the outer nuclear layer. The presence of 3 hyper-reflective bands in the outer retina corresponded to: 1) the external limiting membrane; 2) the cone and rod ellipsoid zones; and 3) the interdigitation zone of photoreceptor outer segments/retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) apical cell processes and the RPE. These correlative and normative SD-OCT data may be employed to characterize and assess the in vivo histologic changes in retinal vascular and degenerative diseases and the responses to novel therapeutic interventions in this large animal model.
Keywords: Anatomy; Eye; Pig; Retinal imaging.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






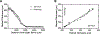
References
-
- Abbott CJ, McBrien NA, Grunert U, Pianta MJ, 2009. Relationship of the optical coherence tomography signal to underlying retinal histology in the tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50, 414–423. - PubMed
-
- Anger EM, Unterhuber A, Hermann B, Sattmann H, Schubert C, Morgan JE, Cowey A, Ahnelt PK, Drexler W, 2004. Ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography of the monkey fovea. Identification of retinal sublayers by correlation with semithin histology sections. Exp Eye Res. 78, 1117–1125. - PubMed
-
- Asami T, Terasaki H, Ito Y, Sugita T, Kaneko H, Nishiyama J, Namiki H, Kobayashi M, Nishizawa N, 2016. Development of a fiber-optic optical coherence tomography probe for intraocular use. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57, 568–574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

