A Critical Role of the IL-1β-IL-1R Signaling Pathway in Skin Inflammation and Psoriasis Pathogenesis
- PMID: 30120937
- PMCID: PMC6392027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.07.025
A Critical Role of the IL-1β-IL-1R Signaling Pathway in Skin Inflammation and Psoriasis Pathogenesis
Abstract
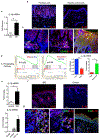
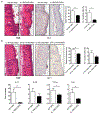
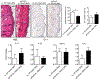
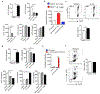
The IL-1 signaling pathway has been shown to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of chronic, autoinflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis. However, the exact cellular and molecular mechanisms have not been fully understood. Here, we show that IL-1β is significantly elevated in psoriatic lesional skin and imiquimod-treated mouse skin. In addition, IL-1R signaling appears to correlate with psoriasis disease progression and treatment response. IL-1 signaling in both dermal γδ T cells and other cells such as keratinocytes is essential to an IMQ-induced skin inflammation. IL-1β induces dermal γδ T cell proliferation and IL-17 production in mice. In addition, IL-1β stimulates keratinocytes to secrete chemokines that preferentially chemoattract peripheral CD27- CCR6+IL-17 capable of producing γδ T cells (γδT17). Further studies showed that endogenous IL-1β secretion is regulated by skin commensals to maintain dermal γδT17 homeostasis in mice. Mouse skin associated with Corynebacterium species, bacteria enriched in human psoriatic lesional skin, has increased IL-1β and dermal γδT17 cell expansion. Thus, the IL-1β-IL-1R signaling pathway may contribute to skin inflammation and psoriasis pathogenesis via the direct regulation of dermal IL-17-producing cells and stimulation of keratinocytes for amplifying inflammatory cascade.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Caccamo N, La Mendola C, Orlando V, Meraviglia S, Todaro M, Stassi G, et al. Differentiation, phenotype, and function of interleukin-17-producing human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells. Blood 2011;118(1): 129–38. - PubMed
-
- Cho KA, Suh JW, Lee KH, Kang JL, Woo SY. IL-17 and IL-22 enhance skin inflammation by stimulating the secretion of IL-1beta by keratinocytes via the ROS-NLRP3-caspase-1 pathway. International immunology 2012;24(3):147–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

