Two Forms of Synaptic Depression Produced by Differential Neuromodulation of Presynaptic Calcium Channels
- PMID: 30122380
- PMCID: PMC7874512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.07.030
Two Forms of Synaptic Depression Produced by Differential Neuromodulation of Presynaptic Calcium Channels
Abstract
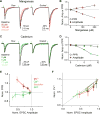
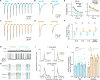
Neuromodulators are important regulators of synaptic transmission throughout the brain. At the presynaptic terminal, neuromodulation of calcium channels (CaVs) can affect transmission not only by changing neurotransmitter release probability, but also by shaping short-term plasticity (STP). Indeed, changes in STP are often considered a requirement for defining a presynaptic site of action. Nevertheless, some synapses exhibit non-canonical forms of neuromodulation, where release probability is altered without a corresponding change in STP. Here, we identify biophysical mechanisms whereby both canonical and non-canonical presynaptic neuromodulation can occur at the same synapse. At a subset of glutamatergic terminals in prefrontal cortex, GABAB and D1/D5 dopamine receptors suppress release probability with and without canonical increases in short-term facilitation by modulating different aspects of presynaptic CaV function. These findings establish a framework whereby signaling from multiple neuromodulators can converge on presynaptic CaVs to differentially tune release dynamics at the same synapse.
Keywords: dopamine; neuromodulation; prefrontal cortex; short-term plasticity; synaptic transmission.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
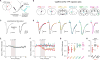
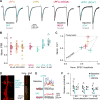
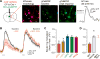
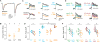


References
-
- Abbott LF, Regehr WG. Synaptic computation. Nature. 2004;431:796–803. - PubMed
-
- Abbott LF, Varela JA, Sen K, Nelson SB. Synaptic depression and cortical gain control. Science. 1997;275:220–224. - PubMed
-
- Allbritton NL, Meyer T, Stryer L. Range of messenger action of calcium ion and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1992;258:1812–1815. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AF, Cai JX, Murphy BL, Goldman-Rakic PS. Dopamine D1 receptor mechanisms in the cognitive performance of young adult and aged monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1994;116:143–151. - PubMed
-
- Barth AL, Poulet JFA. Experimental evidence for sparse firing in the neocortex. Trends Neurosci. 2012;35:345–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

