Narcolepsy and adjuvanted pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 vaccines - Multi-country assessment
- PMID: 30122647
- PMCID: PMC6404226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.08.008
Narcolepsy and adjuvanted pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 vaccines - Multi-country assessment
Abstract
Background: In 2010, a safety signal was detected for narcolepsy following vaccination with Pandemrix, an AS03-adjuvanted monovalent pandemic H1N1 influenza (pH1N1) vaccine. To further assess a possible association and inform policy on future use of adjuvants, we conducted a multi-country study of narcolepsy and adjuvanted pH1N1 vaccines.
Methods: We used electronic health databases to conduct a dynamic retrospective cohort study to assess narcolepsy incidence rates (IR) before and during pH1N1 virus circulation, and after pH1N1 vaccination campaigns in Canada, Denmark, Spain, Sweden, Taiwan, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom. Using a case-control study design, we evaluated the risk of narcolepsy following AS03- and MF59-adjuvanted pH1N1 vaccines in Argentina, Canada, Spain, Switzerland, Taiwan, and the Netherlands. In the Netherlands, we also conducted a case-coverage study in children born between 2004 and 2009.
Results: No changes in narcolepsy IRs were observed in any periods in single study sites except Sweden and Taiwan; in Taiwan incidence increased after wild-type pH1N1 virus circulation and in Sweden (a previously identified signaling country), incidence increased after the start of pH1N1 vaccination. No association was observed for Arepanrix-AS03 or Focetria-MF59 adjuvanted pH1N1 vaccines and narcolepsy in children or adults in the case-control study nor for children born between 2004 and 2009 in the Netherlands case-coverage study for Pandemrix-AS03.
Conclusions: Other than elevated narcolepsy IRs in the period after vaccination campaigns in Sweden, we did not find an association between AS03- or MF59-adjuvanted pH1N1 vaccines and narcolepsy in children or adults in the sites studied, although power to evaluate the AS03-adjuvanted Pandemrix brand vaccine was limited in our study.
Keywords: AS03; Adjuvant; MF59; Narcolepsy; Pandemic H1N1 influenza.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
6. Declaration of interests
Maria de Ridder, Caitlin Dodd, Jan Bonhoeffer, Ann Vanrolleghem, Gert Jan Lammers, Sebastiaan Overeem, Jeffrey C. Kwong, Karen Cauch-Dudek, Diana Juhasz, Michael Campitelli, Wan-Ting Huang, Maria Giner-Soriano, Rosa Morros, Carles Gaig, Ester Tió, Silvia Perez-Vilar, Javier Diez-Domingo, Lawrence W. Svenson, Bruce Carleton, Lisen Arnheim-Dahlström, Lars Pedersen, Frank DeStefano, Tom T. Shimabukuro, Nicoline van der Maas, Brian J. Murray, Alexandre N. Datta, Ulf Kallweit, Yu-Shu Huang, ChungYao Hsu, Hsi-Chung Chen, Francisco Javier Puertas, Monika Naus have no conflicts of interest.
Daniel Weibel, receives consultancy honoraria from GSK for a consultancy related to malaria vaccine implementation in Africa, independent from any flu vaccines, or any work related to this publication.
Angela Gentile, Norberto Giglio, Vanesa Castellano received research contracts from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention independent from this study.
Miriam Sturkenboom received honorarium from GSK and post-authorisation safety studies (PASS) research contracts independent from this study.
Salaheddin M. Mahmud received research funding from GSK, Merck, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi Pasteur and speaking and consulting fees from GSK and Sanofi not related to this study.
Steven Black reports contracts from U.S. Centers for Disease Control, during the conduct of the study; other from GSK Vaccines, outside the submitted work.
Figures
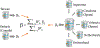
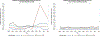
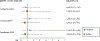
References
-
- Medical Products Agency. A registry based comparative cohort study in four Swedish counties of the risk for narcolepsy after vaccination with Pandemrix – a first and preliminary report, by the Medical Products Agency; 2011. https://lakemedelsverket.se/upload/nyheter/2011/PandemrixRegReport110328....
-
- European Medicines Agency. Pandemrix: EPAR - Product Information; 2016. http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/includes/document/docu....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

