Zafirlukast in combination with pseudohypericin attenuates spinal cord injury and motor function in experimental mice
- PMID: 30122897
- PMCID: PMC6078184
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S154814
Zafirlukast in combination with pseudohypericin attenuates spinal cord injury and motor function in experimental mice
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Zafirlukast in Combination with Pseudohypericin Attenuates Spinal Cord Injury and Motor Function in Experimental Mice [Corrigendum].Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Feb 9;15:419-422. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S304214. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33603335 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Biosynthesis of leukotriene (LT) by arachidonic acid involves 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) as an important precursor. Here, we evaluated the role of pseudohypericin (PHP) for its postulated 5-LO inhibitory activity along with a Cys-LT receptor antagonist zafirlukast (ZFL) against inflammatory response and tissue injury in mice.
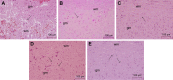
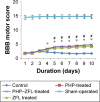
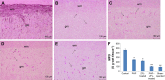
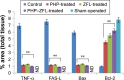
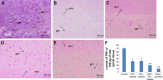
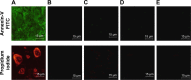
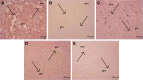
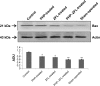
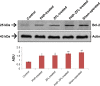
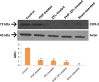
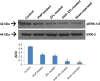
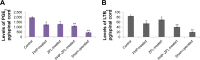
Materials and methods: The spinal injury was induced by two-level laminectomy of T6 and T7 vertebrae. The inflammation was assessed by histology, inflammatory mediators by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, apoptosis by Annexin-V, FAS staining, terminal deoxynucleoti-dyltransferase-mediated UTP end labeling (TUNEL) assay and expression of Bax and Bcl-2 by Western blot. Effect on motor recovery of hind limbs was evaluated for 10 days postinjury.
Results: The spinal injury resulted in tissue damage, apoptosis, edema, infiltration of neutrophils with increased expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). The spinal tissue showed elevated levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and LTB4 and increased phosphorylation of injured extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 (ERK1/2). The PHP, ZFL and combination decreased inflammation, tissue injury and infiltration of neutrophils. Treatment also decreased the levels of PGE2, phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 (pERK 1/2), LT, TNF-α and COX-2 with a marked reduction in apoptosis and improved the motor function.
Conclusion: The present study confirmed 5-LO antagonist activity of PHP and established its neuroprotective role along with ZFL.
Keywords: 5-lipoxygenase; Cys-LT; mice; pseudohypericin; zafirlukast.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Beattie MS. Inflammation and apoptosis: linked therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10(12):580–583. - PubMed
-
- Carlson GD, Gorden C. Current developments in spinal cord injury research. Spine J. 2002;2(2):116–128. - PubMed
-
- Anderson AJ. Mechanisms and pathways of inflammatory responses in CNS trauma: spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2002;25(2):70–79. - PubMed
-
- Jung SB, Song CH, Yang CS, et al. Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in the secretion of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10 by the PPD antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Immunol. 2005;25(5):482–490. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

