Study on the classification of Descemet membrane detachment after cataract surgery with AS-OCT
- PMID: 30123045
- PMCID: PMC6097261
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.26972
Study on the classification of Descemet membrane detachment after cataract surgery with AS-OCT
Abstract
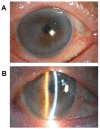
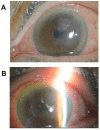
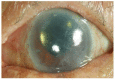
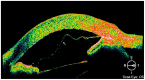
In this article, the significance of anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) to aid the clinical diagnosis and treatment of Descemet membrane (DM) detachment after phacoemulsification combined with intraocular lens implantation was retrospectively analyzed using 26 patients (26 eyes). The location and scope of DM detachment, its causative factors and the percentage of each detachment type are considered for clinical treatments. Based on the location and scope, the detachment can be divided into three types: (1) simple, (2) symmetrical and (3) complete DM detachment. Simple detachment, confined to the area of surgical incision (detachment range <1/4 corneal area), occurred in 69.20 % of cases (18/26), in which the DM detachment in the anterior lip accounted for 42.30% (11/26) and in the posterior lip accounted for 26.90% (7/26). Symmetrical DM detachment, referring to detachment (1/4 cornea area < detached area <1/2 corneal area) that appeared symmetrically on the surgical incision and the opposite site, accounted for 19.20% (5/26). Complete DM detachment (>1/2 of the corneal area), accounted for 11.50% (3/26). Interestingly, our findings suggest that the DM detachment after phacoemulsification is closely related to the location (simple and symmetrical DM detachment) and the skillfulness (complete DM detachment) of the surgical incision. Therefore, appropriate classification of DM detachment by AS-OCT and wise selection of surgical location can better guide cataract surgery in the future.
Keywords: Descemet membrane detachment; anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT); cataract; corneal descension; phacoemulsification.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Blindness as a public health problem in China. 2018.
-
- Jongsareejit A, Wiriyaluppa C, Kongsap P, Phumipan S. Cost-effectiveness analysis of manual small incision cataract surgery (MSICS) and phacoemulsification (PE) J Med Assoc Thai. 2012;95:212–20. - PubMed
-
- Khng CY, Voon LW, Yeo KT. Causes and management of Descemet's membrane detachment associated with cataract surgery-not always a benign problem. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2001;30:532–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

