Urinary Orosomucoid A Potential Marker Of Inflammation In Psoriasis
- PMID: 30123048
- PMCID: PMC6097268
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.25687
Urinary Orosomucoid A Potential Marker Of Inflammation In Psoriasis
Abstract
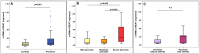
Background: Psoriasis is one of the most common chronic, life-long dermatologic diseases, which has considerable negative effects on quality of life. Psoriasis is considered as a systemic inflammatory disease, thus acute phase proteins such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and orosomucoid (ORM) have been shown to play a role in its pathophysiology. This study was aimed to compare CRP, serum ORM (se-ORM) and urinary ORM (u-ORM) levels of psoriatic patients to healthy individuals. Methods: 87 psoriatic patients and 41 healthy individuals were enrolled. Simultaneously obtained venous blood and spot urine samples were analysed. High sensitivity CRP and se-ORM levels were determined by routine procedures on automated analyzers. Urinary ORM was measured by a novel automated turbidimetric assay. U-ORM was referred to urinary creatinine (u-ORM/u-CREAT, mg/mmol). Results: Significantly higher hsCRP (p<0.001) and u-ORM/u-CREAT (p=0.001) levels were found among psoriatic patients compared to controls. No significant differences were found between the groups regarding se-ORM levels. HsCRP, se-ORM and u-ORM/u-CREAT levels were significantly higher in patients with severe psoriasis than in mild and moderate cases (p<0.05). Conclusion: As a highly sensitive, easily available biomarker u-ORM shows itself capable of becoming a new inflammatory marker in psoriasis providing clinically useful information on disease severity.
Keywords: Orosomucoid; Psoriasis; Urine, Biomarker, Inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Parisi R, Symmons DP, Griffiths CE. et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 2013;133:377–85. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370:263–71. - PubMed
-
- Rapp SR, Feldman SR, Exum ML, Fleischer AB Jr, Reboussin DM. Psoriasis causes as much disability as other major medical diseases. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1999;41:401–7. - PubMed
-
- Shahwan KT, Kimball AB. Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Disease. The Medical clinics of North America. 2015;99:1227–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

