The emerging role of Epstein-Barr virus encoded microRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 30123354
- PMCID: PMC6096363
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.25460
The emerging role of Epstein-Barr virus encoded microRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
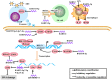
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is an oncogenic herpes virus that is closely associated with the initiation and development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), lymphoma and other malignant tumors. EBV encodes 44 mature miRNAs that regulate viral and host cell gene expression and plays a variety of roles in biological functions and the development of cancer. In this review, we summarized the biological functions and molecular mechanisms of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs (EBV miRNAs) in tumor immune evasion, proliferation, anti-apoptosis, invasion, metastasis and as a potential biomarker for NPC diagnosis and prognosis. The knowledge generated by EBV miRNAs can be used for EBV miRNA-based precision cancer treatments in the near future.
Keywords: EBV miRNAs; anti-apoptosis; biomarker; immune evasion; metastasis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Gong Z, Yang Q, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Li X, Zu X. et al. An integrative transcriptomic analysis reveals p53 regulated miRNA, mRNA, and lncRNA networks in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biology. 2016;37:3683–95. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

