Diagnostic approach to restricted-diffusion patterns on MR imaging
- PMID: 30123680
- PMCID: PMC5829469
- DOI: 10.1212/CPJ.0b013e318278bee1
Diagnostic approach to restricted-diffusion patterns on MR imaging
Abstract
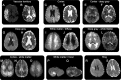
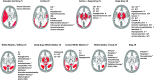
The vast majority of restricted-diffusion abnormalities result from acute stroke, and as such, the diagnosis may be problematic when this MRI feature results from other causes. Distinct patterns of restricted diffusion seen with various disease conditions can play an important diagnostic role. The association of certain diseases with a given restricted-diffusion pattern allows for a focused assessment to determine a specific etiology.
Figures
References
-
- Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 2000;217:331–345. - PubMed
-
- Finelli PF, DiMario FJ. Diagnostic approach in patients with symmetric imaging lesions of the deep gray nuclei. Neurologist 2003;9:250–261. - PubMed
-
- Stadnik TW, Demaerel, Luypaert PR, et al.. Imaging tutorial: differential diagnosis of bright lesions on diffusion-weighted MR images. Radiographics 2003;23:7e. - PubMed
-
- Talbott SD, Plato BM, Sattenberg RJ, Parker J, Heindenreich JO. Cortical restricted diffusion as the predominant MRI finding in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Radiologica 2011;52:336–339. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
