Indole and 2,4-Thiazolidinedione conjugates as potential anticancer modulators
- PMID: 30123711
- PMCID: PMC6087425
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.5386
Indole and 2,4-Thiazolidinedione conjugates as potential anticancer modulators
Abstract
Background: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), also called glitazones, are five-membered carbon ring molecules commonly used for the management of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Recently, many prospective studies have also documented the impact of these compounds as anti-proliferative agents, though several negative side effects such as hepatotoxicity, water retention and cardiac issues have been reported. In this work, we synthesized twenty-six new TZD analogues where the thiazolidinone moiety is directly connected to an N-heterocyclic ring in order to lower their toxic effects.
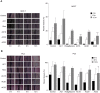
Methods: By adopting a widely applicable synthetic method, twenty-six TZD derivatives were synthesized and tested for their antiproliferative activity in MTT and Wound healing assays with PC3 (prostate cancer) and MCF-7 (breast cancer) cells.
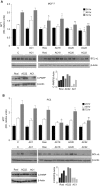
Results: Three compounds, out of twenty-six, significantly decreased cellular viability and migration, and these effects were even more pronounced when compared with rosiglitazone, a well-known member of the TZD class of antidiabetic agents. As revealed by Western blot analysis, part of this antiproliferative effect was supported by apoptosis studies evaluating BCL-xL and C-PARP protein expression.
Conclusion: Our data highlight the promising potential of these TZD derivatives as anti-proliferative agents for the treatment of prostate and breast cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; BCL-xL; Cancer; Cell proliferation; Cellular viability; Thiazolidinediones; Wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Arcidiacono B, Iiritano S, Chiefari E, Brunetti FS, Gu G, Foti DP, Brunetti A. Cooperation between HMGA1, PDX-1, and MafA is essential for glucose-induced insulin transcription in pancreatic beta cells. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2015;5 doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00237. Article 237. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bianconcini A, Lupo A, Capone S, Quadro L, Monti M, Zurlo D, Fucci A, Sabatino L, Brunetti A, Chiefari E, Gottesman ME, Blaner WS, Colantuoni V. Transcriptional activity of the murine retinol-binding protein gene is regulated by a multiprotein complex containing HMGA1, p54 nrb/NonO, protein-associated splicing factor (PSF) and steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1)/liver receptor homologue 1 (LRH-1) International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 2009;41:2189–2203. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.04.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

