Population Pharmacokinetics of the Interleukin-23 Inhibitor Risankizumab in Subjects with Psoriasis and Crohn's Disease: Analyses of Phase I and II Trials
- PMID: 30123942
- PMCID: PMC6373392
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-018-0704-z
Population Pharmacokinetics of the Interleukin-23 Inhibitor Risankizumab in Subjects with Psoriasis and Crohn's Disease: Analyses of Phase I and II Trials
Abstract
Background and objectives: Risankizumab is a humanized anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody in development for the treatment of several inflammatory diseases. This work characterized the pharmacokinetics of risankizumab and evaluated covariates that may affect its exposures using phase I and II trial data in subjects with psoriasis and Crohn's disease.
Methods: Plasma concentration measurements from a phase I study and a phase II study in subjects with psoriasis (n = 157; single doses of 0.01-5 mg/kg intravenously, 0.25-1 mg/kg subcutaneously, and 18 mg subcutaneously, and multiple doses of 90 and 180 mg subcutaneously), and a phase II study in subjects with Crohn's disease (n = 115; doses of 200 or 600 mg intravenously every 4 weeks followed by 180 mg subcutaneously every 8 weeks) were analyzed using non-linear mixed-effects modeling. The model was qualified using bootstrap and simulation-based diagnostics.
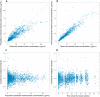
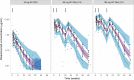
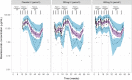
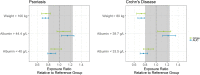
Results: A two-compartment model with first-order absorption and elimination described the pharmacokinetics of risankizumab. Considering the body weight and baseline albumin central tendency differences between disease populations, risankizumab clearance, steady-state volume of distribution, and terminal-phase elimination half-life were estimated to be approximately 0.35 L/day, 11.7 L, and 27 days, respectively, for a typical 90-kg subject with psoriasis with an albumin level of 42 g/L, and 0.31 L/day, 8.45 L, and 22 days, respectively, for a typical 65-kg subject with Crohn's disease with an albumin level of 37 g/L. Risankizumab absolute subcutaneous bioavailability and absorption rate constant were 72% and 0.18 day-1, respectively. Inter-individual variability for clearance was 37%.
Conclusions: Risankizumab displayed pharmacokinetic characteristics typical for an IgG1 monoclonal antibody with no apparent target-mediated disposition. Accounting for the effects of body weight and baseline albumin explained the small differences in the pharmacokinetics of risankizumab between psoriasis and Crohn's disease, with no further differences between the patient populations.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
All authors are employees of AbbVie and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options.
Ethics Approval
Studies included in the analyses were conducted in accordance with Good Clinical Practice guidelines and the ethical principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocols and informed consent forms were approved by the institutional review boards or ethics committees.
Consent to Participate
Participants provided written informed consent before any study-related procedures were performed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Risankizumab in Healthy Volunteers and Subjects with Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Integrated Analyses of Phase I-III Clinical Trials.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Oct;58(10):1309-1321. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00759-z. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 31054118 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Population-Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Tildrakizumab (MK-3222), an Anti-Interleukin-23-p19 Monoclonal Antibody, in Healthy Volunteers and Subjects with Psoriasis.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Aug;58(8):1059-1068. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00743-7. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 30915660 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Risankizumab in Psoriasis Patients.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020 Mar;59(3):311-326. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00842-5. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 31758502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Risankizumab in Asian Healthy Subjects and Patients With Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis, Generalized Pustular Psoriasis, and Erythrodermic Psoriasis.J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;59(12):1656-1668. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1473. Epub 2019 Jun 30. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31257614 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Risankizumab: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2019 Jun;79(8):893-900. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01136-7. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31098898 Review.
Cited by
-
Population Pharmacokinetics and Exposure-Response Analyses for Risankizumab in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis.Rheumatol Ther. 2022 Dec;9(6):1587-1603. doi: 10.1007/s40744-022-00495-0. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Rheumatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36178584 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Risankizumab Treatment in Patients with Crohn's Disease: Results from the Phase 2 Open-Label Extension Study.J Crohns Colitis. 2021 Dec 18;15(12):2001-2010. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab093. J Crohns Colitis. 2021. PMID: 34077509 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Simple Approach to Accurately Predict Pharmacokinetics of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies after Subcutaneous Injection in Humans.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021 Jan;60(1):111-120. doi: 10.1007/s40262-020-00917-8. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2021. PMID: 32779124
-
Spotlight on risankizumab and its potential in the treatment of plaque psoriasis: evidence to date.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2018 Nov 13;8:83-92. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S165943. eCollection 2018. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2018. PMID: 30519540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of IL-23 Pharmacokinetics by Highly Sensitive Accelerator Mass Spectrometry and Subsequent Modeling to Project IL-23 Suppression in Psoriasis Patients Treated with Anti-IL-23 Antibodies.AAPS J. 2019 Jun 27;21(5):82. doi: 10.1208/s12248-019-0352-8. AAPS J. 2019. PMID: 31250228
References
-
- Bowes J, Barton A. The genetics of psoriatic arthritis: lessons from genome-wide association studies. Discov Med. 2010;10(52):177–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

