Emergence of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae, South-Central Ontario, Canada1
- PMID: 30124197
- PMCID: PMC6106407
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2409.180164
Emergence of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae, South-Central Ontario, Canada1
Abstract
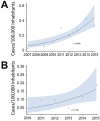
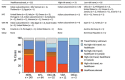
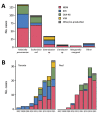
We analyzed population-based surveillance data from the Toronto Invasive Bacterial Diseases Network to describe carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) infections during 2007-2015 in south-central Ontario, Canada. We reviewed patients' medical records and travel histories, analyzed microbiologic and clinical characteristics of CPE infections, and calculated incidence. Among 291 cases identified, New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase was the predominant carbapenemase (51%). The proportion of CPE-positive patients with prior admission to a hospital in Canada who had not received healthcare abroad or traveled to high-risk areas was 13% for patients with oxacillinase-48, 24% for patients with New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase, 55% for patients with Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase, and 67% for patients with Verona integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase. Incidence of CPE infection increased, reaching 0.33 cases/100,000 population in 2015. For a substantial proportion of patients, no healthcare abroad or high-risk travel could be established, suggesting CPE acquisition in Canada. Policy and practice changes are needed to mitigate nosocomial CPE transmission in hospitals in Canada.
Keywords: CPE; Canada; Ontario; antimicrobial resistance; bacteria; bacterial infections; beta-lactam resistance; carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; drug resistance; incidence; population surveillance.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2013. [cited 2018 Mar 19]. http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/ar-threats-2013-508.pdf
-
- World Health Organization. Factsheet on antimicrobial resistance [cited 2018 Mar 19]. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs194
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

