Correlation of Severity of Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Disease and Pathogenicity in Mice
- PMID: 30124404
- PMCID: PMC6106420
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2409.171825
Correlation of Severity of Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Disease and Pathogenicity in Mice
Abstract
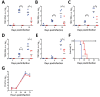
We compared 2 tick-borne encephalitis virus strains isolated from 2 different foci that cause different symptoms in tick-borne encephalitis patients, from neurologic to mild gastrointestinal symptoms. We compared neuroinvasiveness, neurovirulence, and proinflammatory cytokine response in mice and found unique differences that contribute to our understanding of pathogenesis.
Keywords: Germany; Sweden; Tick-borne encephalitis virus; arboviral diseases; flavivirus; pathogenesis; tick-borne encephalitis; ticks; vector-borne infections; viruses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Use of inbred mice for assessing the neurovirulence of strains of the tick-borne encephalitis virus complex and the immunogenicity of a concentrated tick-borne encephalitis vaccine].Vopr Virusol. 1982 Jul-Aug;27(4):461-4. Vopr Virusol. 1982. PMID: 7135927 Russian.
-
Tick-borne encephalitis virus: molecular determinants of neuropathogenesis of an emerging pathogen.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019 Aug;45(4):472-493. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2019.1629872. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31267816 Review.
-
Virulence of tick-borne encephalitis virus is associated with intact conformational viral RNA structures in the variable region of the 3'-UTR.Virus Res. 2015 May 4;203:36-40. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25801453
-
Human Tick-Borne Encephalitis and Characterization of Virus from Biting Tick.Emerg Infect Dis. 2016 Aug;22(8):1485-7. doi: 10.3201/eid2208.151962. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27434395 Free PMC article.
-
Steps of the tick-borne encephalitis virus replication cycle that affect neuropathogenesis.Virus Res. 2005 Aug;111(2):161-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.007. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 15871909 Review.
Cited by
-
Contact-dependent transmission of Langat and tick-borne encephalitis virus in type I interferon receptor-1 deficient mice.J Virol. 2021 Mar 25;95(8):e02039-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02039-20. Epub 2021 Jan 27. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33504602 Free PMC article.
-
Infection of wild-caught wood mice (Apodemus sylvaticus) and yellow-necked mice (A. flavicollis) with tick-borne encephalitis virus.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 7;13(1):21627. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47697-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38062065 Free PMC article.
-
Can Bats Serve as Reservoirs for Arboviruses?Viruses. 2019 Mar 3;11(3):215. doi: 10.3390/v11030215. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30832426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The envelope protein of tick-borne encephalitis virus influences neuron entry, pathogenicity, and vaccine protection.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Sep 28;17(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01943-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32988388 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Early Proinflammatory Responses by TBEV NS1 Varies between the Strains of Various Subtypes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 5;24(2):1011. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021011. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Erber W, Schmitt H-J, Janković TV. Epidemiology by country—an overview. In: Dobler G, Erber W, Schmitt HJ, editors. TBE—the book. Singapore: Global Health Press; 2017. 114–274
-
- Kerbo N, Donchenko I, Kutsar K, Vasilenko V. Tickborne encephalitis outbreak in Estonia linked to raw goat milk, May-June 2005. Euro Surveill. 2005;10:E050623.2. - PubMed
-
- Heinz FX, Kunz C. Tick-borne encephalitis and the impact of vaccination. Arch Virol Suppl. 2004; (18):201–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

